We have shared in-detail CBSE Class 9th English Grammar topic Tenses to help the students hone their grammar structures. We have also shared some basic grammar exercises for class 9th to help the students of class 9th improve their retaining capacity and grammar skills.
Tenses Class 9th is an essential topic of CBSE Class 9th English Grammar to improve the English grammar structures. Basic grammar exercises on tenses in class 9th will help the students improve their questions practice.
Tenses Class 9th English Grammar CBSE
The Tense of a verb tells us when the action is, was, or will be carried out. From the tense of a sentence, we learn about the time of an action. On this page, we are Providing Tense Forms-
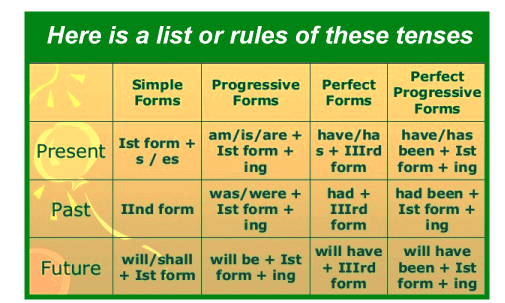
Tenses Class 9th English Grammar CBSE: Introduction
Present Tense
Present Indefinite
This form is used in the case of:
1. things happening in the present Example:
• He is a student.
2. something that happens repeatedly Example:
• He helps his father.
3. a habit or a routine Example:
• He goes to school by bus.
4. describing something that is part of a given situation Example:
• In winter, it gets dark quite early.
5. giving instructions or offering advice Example:
• Take the medicine regularly.
6. stating a permanent truth Example:
• The sun rises in the east.
7. to make future time references when the event is part of a fixed
timetable Example:
• This year, Janamashtami falls on a Sunday.
8. in exclamatory sentences Example:
• Here comes the bus!
9. in commentaries Example:
• Saurav runs forward and takes a catch.
10. instead of present continuous with certain verbs Examples.
• I see smoke. • I have a pen.
The following table shows the different forms of the Present Indefinite Tense.
Affirmative Sentences:
He/She/It + 1st form of the verb + s/es.
Example: He/She/It eats bananas.
I/We/You/They + 1st form of the verb + object.
Example: I/We/You/They eat bananas.
Negative Sentences:
He/She/It does not + 1st form of the verb + object.
Example: He/She/It does not play cricket.
I/We/You/They + 1st form of the verb + object.
Example: I/We/You/They do not play cricket.
Interrogative Sentences:
Do/Does + subject + 1st form of the verb + object + ?
Example :
Do you like to see movies?
Does she like to see movies?
Wh-family + do/does + subject + 1st form of the verb + object +
? Example :
What do you/we/they do with the garbage? What
does she/he do with the garbage?
Note: A Transitive verb requires an object, whereas an Intransitive verb does not, and this rule also applies to present perfect and continuous forms.
Tenses Class 9th Exercises Solved Examples
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. She ………………….. (go) to her office with a friend.
2. Why do you ………………….. (like) movies?
3. My friend ………………….. (visit) his grandmother every day.
4. (do) Ritesh ………………….. (love) the cold weather?
5. …………………. (do) you ………………….. (plan) to visit Kashmir this year?
6. We always ………………….. (have) an early dinner.
7. His parents ………………….. (plan) a trip abroad every six months.
8. Our doctor in the neighborhood………………….. (make) a lot of money.
9. I ………………….. (help) my mother sometimes.
10. Sheetal ………………….. (come) here every Sunday.
11. We ………………….. (eat) rice for dinner every day.
12. He never ………………….. (hide) the truth.
13. Make hay while the sun ………………….. (shine)
14. Apples ………………….. (be) good for health.
Answer:
1. goes
2. do, like
3. visits
4. Does love
5. Do plan
6. have
7. plan
8. makes 9. help
10. comes
11. eat
12. hides
13. shines
14. are
15. bark
16. use
Present Continuous
Usage. The Present Continuous
1. to refer to something happening at the time of speaking Example:
• Please don’t talk so loudly, I am studying.
2. when we talk about something connected with the present time Example:
• These days more and more people are learning a foreign language.
3. when we refer to a situation that is more or less temporary Example:
• She is looking for her spectacles.
4. for an action that is planned for the near future Example:
• I am going to see a movie today.
5. for a persistent habit, Example:
• My dog is rather silly; she is always looking out for an opportunity to forage the
dustbin.
The Present Continuous is formed with the Present Tense of the auxiliary ‘be’ + the present participle.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + Is/Am/Are + 1st form of the verb + ing + object.
Example:
He/She is eating breakfast.
I am eating breakfast.
You/They/We are eating breakfast.
Negative sentences :
Subject + Is/Am/Are + 1st form of the verb + ing + object.
Example:
I am not hitting the ball.
He/She is not hitting the ball.
They/We/You are not hitting the ball.
Interrogative sentences :
Is/Am/Are + subject + 1st form of the verb + ing + object + ?
Example:
Are you/we/they planning a visit to Agra?
Is he/she planning a visit to Agra?
Am I planning a visit to Agra?
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. The CAs (make) a lot of money these days.
2. Why (be) he (not help) you?
3. (be) you (come) to my house today?
4. The band (play) all the old songs.
5. His parents (visit) him today evening.
6. Vijay (behave) very foolishly.
7. By ignoring the traffic signal, they (break) the law.
8. It (rains) heavily outside.
9. Our cook (not come) today.
10. We (face) a lot of problems in our society these days.
11. The driver (plan) to take off tomorrow.
12. I (come) to the party tonight.
13. The children (play) hide and seek in the garden.
14. The train (run) late.
15. Today, the sun (shine) bright.
16. Farmers (plucking) berries from the bushes.
Answer:
1. are making
2. is not helping
3. Are Coming
4. is playing
5. are visiting
6. is behaving
7. are breaking
8. is raining
9. is not coming
10. are facing
11. is planning
12. am coming
13. are playing
14. is running
15. is shining
16. are plucking
Present Perfect
Usage. The Present Perfect Tense is used to or completed in the immediate past.
1. to indicate activities completed in the immediate past Example:
• He has just gone out.
2. to express past actions when no definite time is given Example:
• I have read Gulliver’s Travels.
3. to describe past events that have an impact on the present Examples:
• He has eaten up all the biscuits.
• I have cut my finger.
4. to denote an action that began in the past but continues up to today (using
for, since, etc.) Example:
• I have known him since 1990.
Words often used with the Present Perfect Tense: ‘yet’, ‘so far’, ‘never’, ‘ever’, ‘already’, ‘since’,
‘just now, ‘several times’.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + has/have + 3rd form of the verb + object.
Example:
You/I/We/They have bought the umbrella.
He/She has bought the umbrella.
Negative sentences :
Subject + has have + not + 3rd form of the verb + object.
Example:
You/IJWe/They have not booked the tickets yet.
He/She has not booked the tickets yet.
Interrogative sentences :
Has/have + subject + 3rd form of the verb + object +?
Example:
Have you/I/we/they caught the thief? Has she/he
caught the thief?
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. The cat …………………….. (drink) all the milk.
2. They …………………….. (not arrive) yet.
3. She …………………….. (not qualify) the written test.
4. We …………………….. (be) already …………………….. (see) the movie.
5. I …………………….. (think) of inviting all my friends.
6. My brother …………………….. (not see) the Red Fort yet.
7. The teacher …………………….. (has) just …………………….. (enter) the class.
8. Rajeev …………………….. (stop) learning piano.
9. The media …………………….. (has) just …………………….. (leave) the premises.
10. My parents …………………….. (has/have) recently …………………….. (celebrate) their
fifteenth anniversary.
11. Ramneek …………………….. (lose) the way.
12. The robbers …………………….. (murder) three persons.
13. The minister …………………….. (has) already …………………….. (deliver) his speech.
14. The Sadhus …………………….. (chant) the mantras.
15. Her mother …………………….. (has) not …………………….. (rest).
16. The thief …………………….. (run away).
Answer:
1. has drunk
2. have not arrived
3. has not qualified
4. have, seen
5. have thought
6. has not seen
7. has, entered
8. has stopped
9. has, left
10. have, celebrated
11. has lost
12. have murdered
13. has, delivered
14. have chanted
15. has, rested
16. has run away
Present Perfect Continuous
This form refers to something that began in the past but is still happening at the time
of speaking. Example: I have been reading Gulliver’s Travels for the last week.
Words often used with the Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
Since/for.
Since: suggests the ‘point of time’ for suggests
the ‘period of time.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + has/have + been + ¡st form of the verb + ing + since/for + time.
Example:
Your father has been looking for you for two hours.
They have been looking for you for two hours.
Negative sentences :
Subject + has/have + not + been ÷ ¡st form of the verb ÷ ing + since/for + time.
Example:
The Gardner has not been watering the plants for two hours.
Interrogative sentences :
Has/Have + subject + been + 1st form of the verb + ing + object +?
Example:
Has the grandfather not been taking his medicines?
Wh-family + has/have + subject + been + ¡st form of the verb + ing + object +?
Example:
What has been happening in the office?
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. It ……………………….. (rain) since morning.
2. We ……………………….. (wait) for Rajeev for more than an hour now.
3. Sheela ……………………….. (practice) badminton for three hours.
4. This statue ……………………….. (lying) here for ages.
5. Parul ……………………….. (talk) on the phone for almost one hour.
6. The court ……………………….. (send) the summons for three weeks.
7. The teachers ……………………….. (invigilate) for three hours.
8. These children ……………………….. (suffer) from this allergy for the past one year.
9. I ……………………….. (clean) the classroom since morning.
10. My mother ……………………….. (visit) temples for two weeks now.
11. This playground ……………………….. (lying) in disuse for the past three months.
12. The man in the next room ……………………….. (sing) at 6 o’clock in the morning.
13. I can’t sleep in her room anymore. She ……………………….. (snore) all through.
14. Saheb’s family ……………………….. (wait) at the bus stop since 8 a.m.
15. The patient ……………………….. (sneeze) non-stop.
16. The bikers ……………………….. (race) since the afternoon.
Answer:
1. has been raining
2. have been waiting
3. has been practising
4. has been lying
5. has been talking
6. has been sending
7. have been invigilating
8. have been suffering
9. have been cleaning
10. has been visiting 11. has been lying
12. has been singing
13. has been snoring
14. has been waiting
15. has been sneezing
16. have been racing
Past Indefinite
Usage. The Simple Past (Past Indefinite Tense) is used to.
1. an action completed in the past Example:
• He left for Delhi yesterday.
2. a past habit or a routine Example:
• He went to school by bus but now he walks.
Words often used with the Past Indefinite Tense: Yesterday, ago, last.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. We …………………… (eat) chocolates as a dessert in the party.
2. Kalpana Chawla …………………… (join) NASA as an astronaut.
3. Rowdy students …………………… (break) the furniture of the school last week.
4. I …………………… (live) in the hostel for five years.
5. Sheela’s younger brother …………………… (finish) his homework in the morning.
6. The teacher …………………… (give) a prize to the topper.
7. The dignitaries …………………… (welcome) the guests.
8. The driver of the car …………………… (apply) the brakes.
9. We …………………… (go) to a restaurant for dinner.
10. A massive fire …………………… (break) out in the building yesterday.
11. The educationists …………………… (plan) the syllabus as per the guidelines.
12. Twenty-five jawans …………………… (die) in the avalanche.
13. My father …………………… (buy) an expensive SUV a few days back.
14. The waiter …………………… (clear) the tables after dinner.
15. He never …………………… (lose) sight of the goal.
16. The train …………………… (shake) violently before getting derailed.
Answer:
1. ate
2. joined
3. broke
4. lived
5. finished
6. gave
7. welcomed
8. applied
9. went
10. broke
11. planned
12. died
13. bought
14. cleared
15. lost
16. shook
Past Continuous
Usage. The Past Continuous Tense is used to
1. to refer to something happening at the time of reference in the past Example:
• We were eating our dinner when he came.
2. when we talk about something that was a persistent habit in the past Example:
• He was always grumbling.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + was/were + 1st form of the verb + ing + object.
Example:
He was watching a film.
They were watching a film.
Negative sentences :
Subject + was/were + 1st form of the verb + ing + object Example:
He was not watching a film.
They were not watching a film.
Interrogative sentences :
Was/Were + subject + 1st form of the verb + ing 4- object + ?
Example:
Was he playing cricket in the field?\
Wh-family + was/were + subject + 1st form of the verb + ing + object + ?
Example:
Why were you playing cricket in the field?
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. She …………………… (watch) a movie on television in her bedroom.
2. The thief …………………… (break) the lock when he was caught.
3. Seema …………………… (cook) when the guests entered.
4. What …………………… (be) you …………………… (do) at the railway station?
5. …………………… (be) he …………………… (listen) to the shlokas at the temple?
6. Prem …………………… (play) the instrument when his tutor came.
7. I …………………… (be) busy (wash) clothes when my friend came.
8. The phone …………………… (ring) when the watchman was sleeping.
9. When I went to my friends’ place, they …………………… (sleep).
10. The girl …………………… (drown) when the boatmen saw her.
11. Why …………………… (be) you …………………… (jump) on the road?
12. The Principal …………………… (give away) prizes when the dance troupe came.
13. Where …………………… (be) you …………………… (go) when your mother spotted you?
14. Why …………………… (be) she not …………………… (wear) her raincoat when it was
raining outside?
15. They …………………… (have) their breakfast when the power went off.
16. The children …………………… (not pay) attention in the class.
Answer:
1. was watching
2. was breaking
3. was cooking
4. were, doing
5. was, listening
6. was playing
7. was, washing
8. was ringing
9. were sleeping
10. was drowning
11. were, jumping
12. was giving away
13. were, going
14. was, wearing
15. were having
16. were not paying
Past Perfect
This form is used to indicate the earlier of the two activities that happened in the past.
Example:
• The train had already left by the time I reached the station.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + had + 3rd form of the verb + object.
Example:
He had taken his breakfast when the mother arrived.
Negative Sentence:
Subject + had not + 3rd form of the verb + object.
Example:
He had not taken his breakfast when the mother arrived.
Interrogative sentences:
Had + subject + 3rd form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Had he gone to the theatre?
Wh-family + had + subject + 3rd form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Why had the driver locked the car?
Question 7.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. Why ………………………. (has/have) you ………………………. (not catch) the thief earlier?
2. The king ………………………. (leave) before the prince came.
3. My mother ………………………. (finish) her chores before everybody woke up.
4. The waiter ………………………. (serve) the coffee after everyone finished their meals.
5. ………………………. (has/have) you ………………………. (make) it on time, you would
have got the job?
6. We ………………………. (go) to Manali before the summer approached.
7. When they ………………………. (enter) the room, the music started.
8. My friend ………………………. (purchase) the tickets before the distribution closed.
9. Where ………………………. (has) you ………………………. (go) when I called you up
yesterday.
10. The doctor ………………………. (instruct) the nurses to take special care of the old
patients.
11. The bus driver ………………………. (leave) the bus before it met with an accident.
12. In my childhood, my father would take me to places that I ……………………….
(has/have) not ………………………. (visit)
13. The culprit ………………………. (has) been ………………………. (thrash) before the police
arrived.
14. ………………………. (Has/Have) he not ………………………. (work) hard, he would have
failed.
15. Where ………………………. (have) you ………………………. (disappear) when there was a
party yesterday?
16. The children ………………………. (have pluck) all the flowers before the arrival of the
gardener.
Answer:
1. had, not caught
2. had left
3. had finished
4. had served
5. had, made
6. had gone
7. had entered
8. had purchased
9. had, gone
10. had instructed
11. had left
12. had, visited
13. had, thrashed
14. had, worked
15. had, disappeared
16. had plucked
Past Perfect Continuous
This form is used to refer to something begun in the past and continued up to a point of
reference in the past. Example:
• I had been reading Gulliver’s Travels for the last week when he came to see me.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + had been + ¡st form of the verb ÷ ing + object + since! for + time Example:
I had been waiting for my friend for 3 hours Negative sentences :
Subject + had not been + ¡St form of the verb + ing + object + since! for + time
Example:
I had not been waiting for my friend for 3 hours.
Interrogative sentences :
Had + subject + been + ¡st form of the verb + ing + object + since! for + time?
Example:
Had you been cleaning the place since morning?
Wh-family ÷ had + subject + been + ¡st form of the verb + ing + object + since/for + time?
Example:
Why had the parents been consulting the teacher for so long?
Note: This tense is the same for all persons and can not be used in the passive form and with
verbs that do not have the continuous form.
Question 8.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. Sita …………………… (has) been …………………… (sit) at the computers for five hours
when the bell rang.
2. The doctors …………………… (has) been …………………… (attend) to the patients when
they heard noises outside.
3. The laborers…………………… (has) been …………………… (dig) the site when the wall
came off.
4. Poorvi …………………… (watch) the television when the earthquake came.
5. Parents …………………… (attend) the counseling session when the electricity went
off.
6. The secretary …………………… (look) at the files since morning when the fire alarm
rang.
7. He …………………… (play) guitar for almost five hours when his tutor came.
8. Children …………………… (splash) water in the pool for over three hours.
9. Parents …………………… (worry) about their sick son all day.
10. The typist …………………… (manage) her work for a long time.
11. Children …………………… (play) in the garden since dawn.
12. The car driver …………………… (speed) for quite some time.
13. The grandmother …………………… (sit) in the sun for an hour.
14. The child …………………… (sleep) in the Verandah for three hours.
15. It …………………… (rain) cats and dogs since morning.
16. Why he not …………………… (study) geography in school for so many days?
Answer:
1. had been sitting
2. had been attending
3. had been digging
4. had been watching
5. had been attending
6. had been looking
7. had been playing
8. had been splashing
9. had been worrying
10. had been managing
11. had been playing
12. had been speeding
13. had been sitting
14. had been sleeping
15. had been raining
16. had been studying
Future Indefinite
Usage. The Future Indefinite Tense is used to describe an action that will take place in the
future.
Example :
I shall see you shortly.
He will bring the book.
(a) The future indefinite is also used to express the speaker’s opinion or assumption about the
future.
Example :
Now that the book is in the market, the sales will go up.
(b) to express habitual actions which are likely to take place.
Example :
The sky is overcast, it will rain today.
(c) to express announcements of future plans and weather forecasts.
Example :
The floodwaters will continue to recede how.
Words often used with the future indefinite tense: tomorrow, next
Affirmative sentences
Subject + will/shall + 1st form of the verb + object Example:
He will arrive any time now. I shall fast tomorrow.
Negative sentences
Subject + will/shall not + 1st form of the verb + object Example:
They will not perform the puja today; interrogative sentences
will/shall + subject + 1st form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Will they attend school tomorrow?
Wh-family + will/shall + subject + 1st form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Why will they go out in the rain?
Question 9.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. Mumbai Indians team ……………………. (play) against Pune Supergiants on Thursday.
2. I ……………………. (leave) for Kolkata next week.
3. The children ……………………. (go) for a picnic tomorrow.
4. The prizes ……………………. (be) distributed after the exams.
5. …………………… we place the order?
6. Why ……………………. (he tell) a lie?
7. My father ……………………. (buy) the lottery ticket in the evening.
8. I ……………………. (not eat) my dinner tonight.
9. She ……………………. (recite) the poem in her school.
10. Ramesh ……………………. (resolve) the issue.
11. Poorvi ……………………. (attend) the wedding next Sunday.
12. My parents ……………………. (visit) the shrine tomorrow.
13. You ……………………. (receive) your books through courier.
14. I ……………………. (not visit) the doctor today.
15. Prerna ……………………. (tie) Rakhee to her stepbrother also.
16. Raju ……………………. (finish) his work by noon.
Answer:
1. will play
2. shall leave
3. will go
4. will be
5. Shall
6. will he tell
7. will buy
8. will not eat
9. will recite
10. will/shall resolve
11. will attend
12. shall visit
13. shall receive
14. will not visit
15. will tie
16. will finish
Future Continuous
Usage. The Future Continuous Tense like the other continuous tense is used with a point of
time. It expresses an action that will be going on at the time of speaking.
Example:
Puja will be reading a book at that time.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + will/shall + be 4- 1st form of the verb + ing + object .
Example:
You shall be giving the lecture tonight Negative sentences
:
Subject + will/shall 4r,not + be + 1st form of the verb + ing + object Example:
He will not be giving the lecture tonight.
Interrogative sentences :
Will/Shall + subject + be + 1st form of the verb + ing + object + ?
Example:
Will they be playing in the ground in that heat?
Wh-family + will/shall + subject + be + 1st form of the verb + ing +object + ?
Example:
Why will he be objecting to her joining the army?
Question 10.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. She ……………………. (help) her mother in the kitchen.
2. The organizers……………………. (introduce) the guests at the function.
3. The florist ……………………. (deliver) the bouquet by afternoon.
4. Sunita ……………………. (do) her homework shortly.
5. I ……………………. (watch) the match tonight.
6. My parents ……………………. (arrive) by the morning flight tomorrow.
7. India ……………………. (soon compete) with the superpowers.
8. He ……………………. (turn) eighteen next month.
9. The officials ……………………. (visit) the school in the morning.
10. She is vomiting. She ……………………. (fall) sick anytime.
11. Gopal ……………………. (drive) all the way to Kanpur.
12. My brother ……………………. (leave) for his foreign assignment in a day or two.
13. When ……………………. you be ……………………. participate in the competition?
14. I ……………………. (wait) for you downstairs.
15. The movie ……………………. (releasing) next Friday.
16. The principal ……………………. (address) a group of parents on Saturday.
Answer:
1. will be helping
2. will be introducing
3. will be delivering
4. will be doing
5. will be watching
6. will be arriving
7. will soon be competing 8. will be turning.
9. will be visiting
10. will be falling
11. will be driving
12. shall be leaving
13. will, participating
14. shall be waiting
15. will be releasing
16. will be addressing
Future Perfect
Usage. The Future Perfect Tense is used to express an action that will have been completed in
the future by a certain time.
Example:
By tomorrow, I shall have bought a new bicycle.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + will/shall + have + 3rd form of the verb + object Example:
At this time tomorrow, she will have left for the US.
Negative sentences :
Subject + will/shall + net + have + 3rd form of the verb + object Example:
I will not have reached the airport in two hours.
Interrogative sentences :
Will/Shall + subject + have + 3rd form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Will he have practised for the dance performance?
Wh-family + will/shall + subject + have + 3rd form of the verb + object + ?
Example:
Where shall I have gone in search of food?
Note: First-person ‘shall’ may be used in place of ‘will’.
Question 11.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. I ……………………. (decide) to leave by tomorrow morning.
2. She ……………………. (finish) her cooking by the time I reach her place.
3. The thieves ……………………. (steal) the money by the time the police arrives.
4. By next week, he ……………………. (quit) his job.
5. In the coming years, doctors ……………………. (discover) a cure for cancer.
6. The tournament ……………………. (begin) by then.
7. In another ten years, bullet trains ……………………. (become) a common sight.
8. The judge ……………………. (pass) the judgment by afternoon.
9. The minister ……………………. (visit) the shrine by 6 o’clock.
10. The train ……………………. (reach) the station by the time we reach.
11. The doctors ……………………. (perform) the operation seeing the condition of the
patient.
12. The priest ……………………. (finish) the prayers before more people gathered at the
church.
13. The lioness ……………………. (attack) its prey to feed its cubs.
14. He ……………………. (return) the book by tomorrow morning.
15. The king ……………………. (visit) the palace before the arrival of the enemies.
Answer:
1. shall have decided
2. will have finished
3. shall have stolen 4. will not have gone.
5. will have quit
6. will have discovered
7. will have begun
8. will have become
9. will have passed
10. will have visited
11. will have reached
12. will have performed
13. shall have finished
14. will have attacked
15. will have returned
16. will have visited
Future Perfect Continuous
Usage. The Future Perfect Continuous Tense denotes an action that will be finished at some
definite time in the future, but which had been going on before it was finished.
Example:
Tomorrow night, he will have been watching the show at the ‘Kingdom of Dreams’.
Affirmative sentences :
Subject + will/shall + have been + 1st form of the verb + ing+ object Example:
You will have been celebrating your birthday tomorrow this time.
Negative sentences :
Subject + will/shall not + have been + ¡st form of the verb + ¡ng + object Example:
The program will not have been going on without the manager’s consent.
Interrogative sentences :
Will/Shall + subject + have been + ¡st form of the verb ÷ ing + object +?
Example:
Will the Censor Board have been objecting to the obscene scenes in the film?
Wh-family + will/shall + subject + have been + ¡st form of the verb + ing + object +?
Example:
When will you have been giving the statement in court? Note: ‘shall’
may be used for first-person.
Question 12.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
1. I ………………………….. (revise) my syllabus by the end of the term.
2. He ………………………….. (Play) with his friends for nearly 3 hours.
3. The laborers………………………….. (dig) the pit for close to five hours.
4. Shyam ………………………….. (reach) by evening time.
5. The postman ………………………….. (deliver) the parcel next week.
6. ………………………….. (will) you ………………………….. (run) the marathon tomorrow
morning for six hours?
7. We ………………………….. (see) the ‘London Bridge’ by tonight.
8. I ………………………….. (do) the shopping for almost the entire day.
9. You ………………………….. (celebrate) your anniversary tomorrow.
10. Tomorrow, at this time we ………………………….. (drive) to Haridwar for three hours.
11. My mother ………………………….. (prepare) for a party next week this time.
12. When you meet me next, I ………………………….. (complete) my research shortly.
13. He ………………………….. (play) chess with his friend tomorrow.
14. The sun ………………………….. (set) by the time we finish our work.
15. We ………………………….. (shop) in Mumbai tomorrow, when you reach here.
16. My uncle ………………………….. (cover) the distance to Nainital before we reach
there.
Answer:
1. shall have been revising
2. will have been playing
3. shall have been digging
4. will have been reaching
5. will have been delivering
6. Will have been running
7. will have been seeing
8. shall have been doing
9. will have been celebrating
10. shall have been driving
11. will have been preparing
12. shall have been completing
13. will have been playing
14. will have been setting
15. will have been shopping
16. will have been covering
Tenses Class 9th English Grammar CBSE: Practice Questions
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets.
Question 1.
Once when I (a) ………………………….. (cross) the road, I (b) ………………………….. (see) a small boy
who (c) ………………………….. (look) quite lost. I (d) ………………………….. (ask) him the name of his
parents but he (e) ………………………….. (can) not answer. After waiting for a little while, I (f)
………………………….. (bring) him home and (g) ………………………….. (feed) him.
Answer:
(a) was crossing
(b) saw
(c) looked
(d) asked
(e) could
(f) brought (g) fed
Question 2.
I (a) ………………………….. (feel) very sorry to see the pathetic condition of the slums. Children
(b) ………………………….. (be) shabbily dressed and were running all over the place. A small
girl (c) ………………………….. (eat) a banana. She (d) ………………………….. (get) it from her father.
Her father (e) ………………………….. (be) a poor laborer. Her mother always (f)
………………………….. (remain) sick. Answer:
(a) felt
(b) were
(c) was eating
(d) had got
(e) was (f) remained
Question 3.
As per the prediction of the Met. Department, it (a) ………………………….. (rain) tomorrow. On
hearing this, the farmers (b) ………………………….. (start) dancing. There (c) ………………………….. (be)
no rains in their area for a long time. This weather prediction (d) …………………………..
(make) everybody happy.
Answer:
(a) will rain
(b) started
(c) had been (d) made
Question 4.
Seema, my classmate is (a) ………………………….. (celebrate) her birthday tomorrow. I (b)
………………………….. (want) to gift her a science puzzle but (c) ………………………….. (not know)
where to buy it from. I (d) ………………………….. (will/shall) ask my father in the evening when he
(e) ………………………….. (return) home from work.
Answer:
(a) celebrating
(b) want
(c) do not know
(d) shall
(e) returns
Question 5.
It’s a bright afternoon. The sun (a) ………………………….. (shine) in the sky. The children (b)
………………………….. (Play) in the garden where there (c) ………………………….. (be) lots of plants.
Squirrels (d) ………………………….. (nibble) at the small pieces of food. The place (e)
………………………….. (be) buzzing with activity. We (f) ………………………….. (be) all very happy and
enjoying the place.
Answer:
(a) is shining
(b) are playing
(c) are
(d) are nibbling
(e) is
(f) are
Question 6.
Two children (a) ………………………….. (be) playing in the backyard of their house when they
(b) ………………………….. (spot) a tiger cub. Mistaking it for a big cat, they (c)
………………………….. (bring) it home and (d) ………………………….. (hide) it. When their parents (e)
………………………….. (come back) in the evening, they (f) ………………………….. (decide) that they (g)
………………………….. (will/shall) not disclose the presence of the big cat to their parents. Answer:
(a) were
(b) spotted (c) brought
(d) hid
(e) came back
(f) decided (g) would
Question 7.
The students (a) ………………………….. (organize) a rally to bring awareness among the locals
regarding pollution. Many junior students also (b) ………………………….. (join) it- They (c)
………………………….. (stage) a street play which (d) ………………………….. (appreciate) by one and
all. All the activities (e) ………………………….. (be) very successful. These (f) ………………………….. (be
aim) to bring about awareness among people.
Answer:
(a) have organised/organised
(b) joined
(c) staged
(d) was appreciated (e) were (f) were aimed
Question 8.
We all (a) ………………………….. (need) change as it (b) ………………………….. (refresh) and (c)
………………………….. (relax) our minds. Schools and colleges too give long holidays to students to
(d) ………………………….. (rejuvenate) themselves, holidays (e) ………………………….. (be) a welcome
change. In our country, we (f) ………………………….. (be) number of holidays, on account of
religious and national festivals.
Answer:
(a) need
(b) refreshes
(c) relaxes
(d) rejuvenate
(e) are (f) have
Question 9.
An old couple (a) ………………………….. (cross) the road when a speeding truck (b)
………………………….. (hit) them from behind. The old man (c) ………………………….. (fly) into the air
while the woman (d) ………………………….. (lie) bleeding on the ground. People (e)
………………………….. (gather) and (f) ………………………….. (take) them to the hospital where they (g)
………………………….. (declare) brought dead. Answer:
(a) was crossing
(b) hit
(c) was flung
(d) was lying
(e) gathered
(f) took
(g) were declared
Question 10.
Romila (a) ………………………….. (go) to a hotel to celebrate her birthday in the evening. Many
guests (b) ………………………….. (invite). Her father (c) ………………………….. (buy) a new dress for her
and the mother (d) ………………………….. (order) a chocolate cake. Today she (e)
………………………….. (turn) sixteen. She remembers that last year, she (f) …………………………..
(gift) a bicycle by her parents. Answer:
(a) went
(b) were invited
(c) bought
(d) ordered
(e) turns/turned (f) was gifted
Question 11.
What (a) ………………………….. (do) you do if there (b) ………………………….. (be) nobody to
receive you at the railway station? (c) ………………………….. (Will/Shall) you take a cab on your
own or (d) ………………………….. (will/shall) you wait there? You (e) ………………………….. (not
carry) much luggage but the one bag that you (f) ………………………….. (be) is quite heavy.
Answer:
(a) do
(b) is
(c) Will
(d) will
(e) are not carrying (f) have
Question 12.
Rosy (a) ………………………….. (fell) sick so her mother (b) ………………………….. (take) her to a nearby
doctor. The doctor said, “You (c) ………………………….. (must) take the medicines regularly and (d)
………………………….. (drink) lots of fluid.” Rosy (e) ………………………….. (not pay) much attention to
the doctor’s words which (f) ………………………….. (make) he scolds her.
Answer:
(a) had fallen
(b) took
(c) must (d) drink
(e) did not pay (f) made
Conclusion
We have shared Tenses class 9th –CBSE Class 9th English Grammar along with practice questions to help their students to be able to hone their grammar structures, and we have also penned down Tenses Class 9th English Grammar CBSE so they would be able to polish their contextual grammar skills.
Related Articles
- Article Writing Class 9th English CBSE
- Discursive Writing Class 12th English
- Notice Writing Format Class 9th English
- Report Writing Class 12th Format

