We provide you with the best resources related to the social science history lesson 3 Nazism and the rise of Hitler. In this article, we will talk about the birth of the Weimar Republic, the rise of Hitler, and the consequent changes related to this. We will also highlight the policy of the Nazis and its effects on the minds of youth and women. These will help the students take hold of the concepts and prepare for their exams. it will hone your concepts, and you will be able to get the gist of the lesson Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9.
Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9: Introduction
Birth of the Weimar Republic
In the early years of the twentieth century, Germany fought the First World War (1914-1918) alongside the Austrian empire and against the Allies (England, France and Russia.). The war drained out all their wealth and led them to debt.. Germany got hold of France and Belgium. With the US entry, Germany and the central powers lost the war. At Weimar, the National Assembly met and established a democratic constitution with a federal structure. The War Guilt Clause held Germany responsible for the war and damages the Allied countries suffered. The Allied armies occupied Rhineland in the 1920s.
The Effects of the War
The entire continent was devastated by the war both psychologically and financially. Heavy expenses on the defense caused them to pay off the debts as soon as possible. Socialists, Catholics and Democrats, supported the Weimar Republic, and they were mockingly called the ‘November criminals. The First World War left a deep imprint on European society and polity. Soldiers are placed above civilians, but unfortunately, soldiers live a miserable life. Democracy was a young and fragile idea for them; it was at its infant stage and could not be understood by the german people.
Political Radicalism and Economic Crises
They crushed the uprising with the help of a war veterans organization called Free Corps. Communists and Socialists became enemies. Political radicalization was heightened by the economic crisis of 1923. When Germany refused to pay, France occupied its leading industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicized evoking worldwide sympathy. This crisis came to be known as hyperinflation, a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.
The Years of Depression
The years between 1924 and 1928 saw some stability. But it was short term as soon as the great depression hit the USA, they withdrew all support. The national income of the USA fell by half, and all were shut down till the recession. The economy of Germany was the worst hit. Workers became jobless and went on streets with placards saying, ‘Willing to do any work. Youth indulge themselves in criminal activities. The middle class and small businessmen were filled with the anxiety of being reduced to the working class ranks or unemployment. Politically also the Weimar Republic was fragile.
Inherent defects of the Weimar republic
The Weimar constitution’s inherent defects made it unstable and vulnerable to dictatorship. One inherent defect was proportional representation. Another defect was Article 48, which gave the President the powers to impose an emergency, suspend civil rights, and rule by decree.
Hitler’s Rise to Power
- Hitler was born in 1889 in Austria and spent his youth in poverty. During the first world war he joined as a messenger and also earned a medal for his valor.Hitler joined a small group called the German Workers’ Party in 1919.
- He renamed the organization the National Socialist German Workers’ Party, later known as the Nazi Party.
- The great depression gave him a chance to rise to power, so he planned to march Berlin by seizing Bavaria in 1923.. During the Great Depression, Nazism became a mass movement.
- After 1929, banks collapsed, businesses shut down, workers lost their jobs and the middle classes were threatened with destitution. In such a situation, people saw hope in Hitler and called him a messiah. He showed them hopes of better tomorrow.
- Hitler possessed the gift of the gab and his words moved people. In his speech, he promised to build a strong nation, undo the injustice of the Versailles Treaty and restore the dignity of the German people.
- He promised employment for the youth and gave them hope for a better future. He also promised to nip off the bud who conspired against Germany.
- Hitler started following a new style of politics, and his followers held big rallies and public meetings to demonstrate support.
- According to the Nazi propaganda, Hitler was called a messiah, a savior, who cab heal their wounds of all distress.
Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9:The Enabling Act Of 1933
President Hindenburg offered the Chancellorship, on 30 January 1933, the highest position in the cabinet of ministers, to Hitler. On 3 March 1933, the famous Enabling Act was passed, establishing a dictatorship in Germany. The state took control of everything from the economy to the judiciary. Apart from the already existing regular police in green uniform and the SA or the Storm Troopers, these included the Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads), criminal police and the Security Service (SD).
Reconstruction of Economy
To recover the ailments of the economy he gave the responsibility to Hjalmer Sacht who promised full employment and full production through state fund work programs. This project produced the famous German superhighways and the people’s car, the Volkswagen. Hitler ruled out the League of Nations in 1933, reoccupied the Rhineland in 1936, and again merged Austria and Germany in 1938 under the slogan, One people, One empire and One leader. Schacht was removed by the hitler as he advised him as the state was running on huge deficits.
The Nazi Worldview
According to the Nazi ideologies, they all follow different practices. There was no question of equality but he believed in the racial hierarchy propounded by Charles darwin and herbert spencer.
They wanted the most potent race to survive as he wanted to lead german with the most vital race. He wished and wanted to perish all others. Hitler considered the Aryan race superior; all others were primitive and needed to be thrown out.
He also wanted to extend its territories by moving eastwards to concentrate all germans at one place and not to be distributed here and there.
Establishment of the Racial State
Nazi came to power and wanted to create a community of pure Germans. He wanted that only healthy and pure nordic Aryans should rule the Germans and only they are needed. Under the Euthanasia Programme, Helmuth’s father was engaged in giving death to many Germans who were considered mentally or physically unfit.
Germany occupied Poland and parts of Russia, captured civilians, and forced them to work as slave labor. Jews remained the worst sufferers in Nazi Germany. Hitler hated Jews based on pseudoscientific theories of race. From 1933 to 1938, the Nazis terrorized, pauperized and segregated the Jews, compelling them to leave the country.
The Racial Utopia
Genocide and war became two sides of the same coin. Poland was divided and much of north-western Poland was annexed to Germany.
They were forced to leave their country, and many were killed in the concentration camps. Polish children who looked like Aryans were given to foster families after being examined by race experts.
Youth in Nazi Germany
Hitler was interested in the youth as he believed that posterity can lead Germany to its zenith. He started playing with their young, innocent minds.
He added Nazi policies and its justification in the school books and curriculum. Jews were not allowed to sit and talk with the Aryans.
Children were taught to loyal, polite toward Hitler and hate jews and, gypsies and other race. The spirit of nationalism was inculcated in them through youth organizations.
The boys needed to join Nazi Youth Organisation and were taught to worship their ideas and Hitler. They were also taught to hate the other races.
At the age of 18 they also needed to join the labor service and serve in the army to enter one of the Nazi Organisations.
The Nazi Cult of Motherhood
In Nazi Germany, children were told women were different from men. Boys were taught to be aggressive, masculine and steel hearted and girls were told to become good mothers and rear pure-blooded Aryan children.
Girls had to maintain the purity of the race, distance from Jews, look after their home and teach their children Nazi values. But all mothers were not treated equally. Honors Crosses were awarded to those who encouraged women to produce more children. Bronze cross for four children, silver for six, and gold for eight or more.
Women who maintained contact with Jews, Poles, and Russians were paraded through the town with shaved heads, blackened faces, and placards hanging around their necks announcing ‘I have sullied the honor of the nation’.
The Art of Propaganda
Nazis termed mass killings as special treatment, final solution (for the Jews), euthanasia (for the disabled), selection, and disinfection. ‘Evacuation’ meant deporting people to gas chambers. Gas chambers were labeled as ‘‘disinfection-areas’, and looked like bathrooms equipped with fake showerheads.
They spread their ideas through visual images, films, radio, posters, catchy slogans, and leaflets. Orthodox Jews were stereotyped and marked and were referred as inferiors. The Nazis made equal efforts to appeal to all the different sections of the population. They sought to win their support by suggesting that Nazis alone could solve all their problems.
Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity
Soon people also spoke his language and supported his ideas, might be due to fear or through their own rationale. They started feeling hate towards jews and other races. They all believed that Hitler and the Nazi party would make them happy and sort out their problems.
Some still believed that Hitler was wrong and he was doing a big crime against humanity, like Pastor Niemoeller protested against brutal and organized crimes committed in the Nazi empire. Charlotte Beradt’s book called the Third Reich of Dreams describes how Jews themselves began believing in the Nazi stereotypes about them. They started believing that they were inferior and bad.
Knowledge about the Holocaust
When the war ended with the defeat of Germany, Jews wanted the world to know how much they all had suffered due to Nazi killing operations, which they termed as Holocaust.
When they lost the war, petrol was distributed to the officials to destroy the evidence, if any left.
Ncert Solutions For Class 9th Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler
Q1. Describe the problems faced by the Weimar Republic.
- A National Assembly met at Weimar and established a democratic constitution with a federal structure. Deputies were now elected to the German Parliament or Reichstag, based on equal and universal votes cast by all adults, including women.
- However, it was not received well by its people largely because of the terms it was forced to accept after Germany’s defeat at the end of the First World War.
- The peace treaty at Versailles with the Allies was a harsh and humiliating peace. Germany lost its overseas colonies, a tenth of its population.
- The Allied Powers demilitarised Germany to weaken its power. The War Guilt Clause held Germany responsible for the war and damages the Allied countries suffered. Germany was forced to pay compensation amounting to £6 billion.
- The Allied armies also occupied the resource-rich Rhineland for much of the 1920s. Many Germans held the new Weimar Republic responsible for not only the defeat in the war but the disgrace at Versailles.
Q2. Discuss why Nazism became popular in Germany by 1930?
- The great depression gave Hitler a chance to rise to power, so he planned to march Berlin by seizing Bavaria in 1923. During the Great Depression, Nazism became a mass movement.
- After 1929, banks collapsed, businesses shut down, workers lost their jobs, and the middle classes were threatened with destitution. In such a situation, people saw hope in Hitler and called him the messiah. He showed them hopes of better tomorrow.
- Hitler possessed the gift of the gab and his words moved people. In his speech, he promised to build a strong nation, undo the injustice of the Versailles Treaty and restore the dignity of the German people.
- He promised employment for the youth and gave them hope for a better future. He also promised to nip off the bud who conspired against Germany.
- Hitler started following a new style of politics, and his followers held big rallies and public meetings to demonstrate support.
- According to the Nazi propaganda, Hitler was called a messiah, a savior, who cab heal their wounds of all distress.
Question 3. What are the peculiar features of Nazi thinking?
According to the Nazi ideologies, they all follow a different set of practices. There was no question of equality, but he believed in the racial hierarchy propounded by Charles darwin and herbert spencer.
They wanted the most potent race to survive as he wanted to lead german with the most vital race. He wished and wanted to perish all others.
Hitler considered the Aryan race superior; all others were primitive and needed to be thrown out.
He also wanted to extend its territories by moving eastwards to concentrate all germans in one place and not to be distributed here and there.
However, his ideas were used by racist thinkers and politicians to justify imperial rule over conquered peoples. The Nazi argument was simple: the most vital race would survive and the weak ones would perish. The Aryan race was the finest. It had to retain its purity, become more robust and dominate the world. He also wanted to acquire the lebensraum so that all Germans could be at one place so for this he tried to move eastward to imperialize.
Question 4. Explain why Nazi propaganda was effective in creating a hatred for Jews.
- They used the words very cunningly to deceive the media and never used straight words like murder or kill in their official communications.
- Mass killings were also termed as final solutions or euthanasia. The word evacuation means taking people to gas chambers. They used the media by catchy slogans and films and documentaries to avoid them. They also showed socialists and liberals weak and enemies to them.
- Jews’ homes were marked, and they were shown as inferior with long beards wearing kaftans and mocked their outer appearance. They were termed rodents, vermin and stereotyped in many ways as possible.
- Nazism played with people’s emotions and used this to turn them against each other. They made equal appealing efforts to win their support and showed themselves as their savior.
Question 5. Explain what role women had in Nazi society. Return to Chapter 1 on the French Revolution. Write a paragraph comparing and contrasting the role of women in the two periods.
- Children in Nazi Germany were repeatedly told that women were radically different from men. The fight for equal rights for men and women that had become part of democratic struggles everywhere was wrong and it would destroy society.
- While boys were taught to be aggressive, masculine and steel-hearted, girls were told that they had to become good mothers and rear pure-blooded Aryan children.
- Girls had to maintain the purity of the race, distance themselves from Jews, look after the home, and teach their children Nazi values. They had to be the bearers of the Aryan culture and race.
- Women who bore racially undesirable children were punished and those who produced racially desirable children were awarded.
- All ‘Aryan’ women who deviated from the prescribed code of conduct were publicly condemned and severely punished. Those who maintained contact with Jews, Poles, and Russians were paraded through the town with shaved heads, blackened faces, and placards hanging around their necks announcing ‘I have sullied the honor of the nation’.
- Many received jail sentences and lost civic honor and their husbands and families for this ‘criminal offense’. This scenario was completely different from the role of women in the French Revolution, where women played essential roles in many movements. They fought for equal rights and wages.
Question 6. In what ways did the Nazi state seek to establish total control over its people?
- On 3 March 1933, the famous Enabling Act was passed. This Act established a dictatorship in Germany. It gave Hitler all powers to sideline Parliament and rule by decree.
- All political parties and trade unions were banned except for the Nazi Party and its affiliates. The state established complete control over the economy, media, army and judiciary.
- Special surveillance and security forces were created to control and order society in ways that the Nazis wanted. Apart from the already existing regular police in green uniform and the SA or the Storm Troopers, these included the Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads), criminal police, and the Security Service (SD).
- The extra-constitutional powers of these newly organized forces gave the Nazi state its reputation as the most dreaded criminal state.
- People could now be detained in Gestapo torture chambers, rounded up and sent to concentration camps, deported at will, or arrested without any legal procedures. The police forces acquired powers to rule with impunity.
Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9 Map Work
Major Countries of Second World War
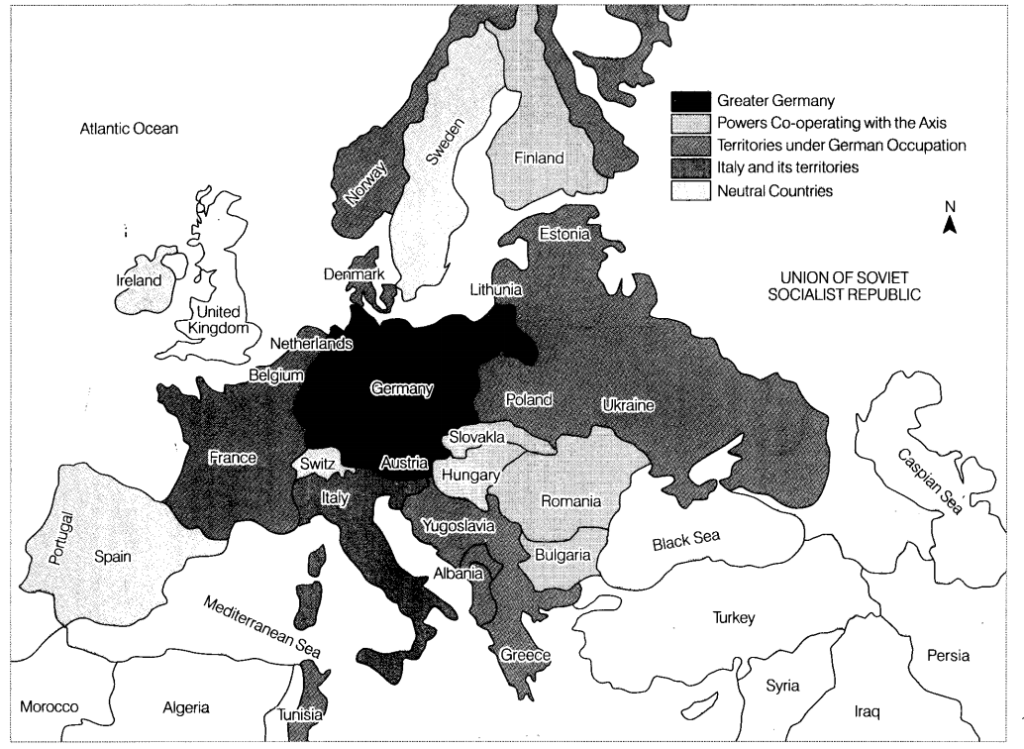
Q1. On the outline map of the world, locate and label the countries that were Axis Powers in the Second World War.
Answer: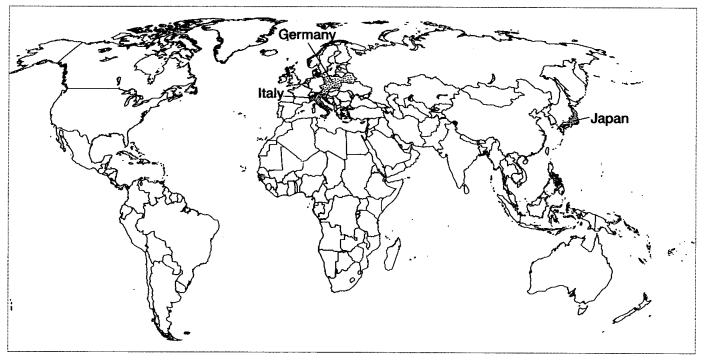
Q2. On the outline map of Europe, certain features are marked. These are the countries that were once territories under German expansion. Identify them.
Answer: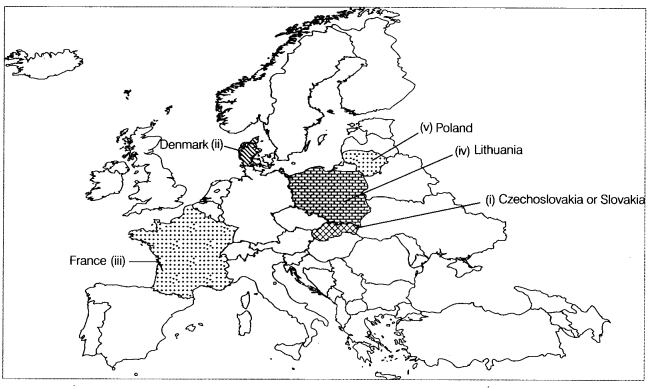
Q3. On the outline map of Europe, certain features are marked. These are the countries that were once territories under German expansion. Identify them.
Answer: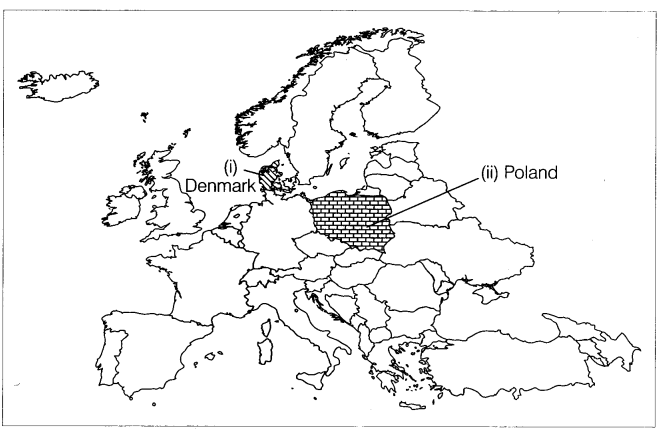
Conclusion
In the above article, we have provided you with the Ncert Solutions For Class 9th Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler and short but detailed notes on Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9. Students can get help and clarify their concepts after they review these notes and answers. We also did map work to help them know the geographical view and the lesson’s events.
Related Articles

