We are providing you with the short and detailed notes of Natural Resources class 9 Biology along with the solutions of back exercises to give a crystal clear idea to the students to be able to attempt questions in the examination.
In this lesson, we will lay thrust upon natural resources that exist on our mother earth, how we need to consume them, and what are the ways of using them sustainably.
Introduction
Life exists on earth due to its favourable conditions that are suitable for our planet earth, like distance from the sun, water, food and energy from the sun.
Lithosphere- The outer crust of the earth is called the lithosphere.
Hydrosphere- The sum of all water bodies is called hydrosphere.
Atmosphere- The air that covers the earth is called the atmosphere.
Biosphere- The life-supporting zone of the earth where the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere interact and make life possible is called the biosphere. It consists of biotic components-living things and abiotic components-non- living things like air, water and soil
Air- It is a mixture of many gases like oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases.
- Nitrogen is used by plants for protein synthesis.
- Oxygen sustains life used for respiration, combustion.
- The carbon dioxide is used by plants for preparing food by photosynthesis.
Water vapour- provides moisture. It also varies from one place to another.
Atmosphere- Acts as a protective blanket around the earth. Maintains the temperature on the surface of the earth. Winds are caused due to uneven heating of the atmosphere, these winds maintain the pressure difference and cause cold and hot air, sea and land breeze, brings rain etc.
Rain- The clouds formed due to the evaporation of water condenses and precipitates as rain.
Water- Various sources of water are available i.e., surface water, underground water, snow, icebergs, water vapour in the atmosphere.
Use of Water
- Water is used for transportation.
- Sustain life
- Used by plants and animals for life processes. Water available for drinking should be conserved and used wisely.
Soil- Soil is formed by a very slow process i.e., by weathering of rocks. It consists of various nutrients. Plants grow in the soil, many microbe’s homes are soil.
Varieties of soil types are available
As per the Indian climate, we are blessed with many types of soil and depending on the texture and chemical properties we use them for various purposes.
- Sandy soil
- Loamy Soil
- Clayey Soil
- Black soil
- Red soil
- Alluvial soil
- Laterite soil.
Temperature- Temperature and light are also required for all biotic components.
Pollution- Contamination of natural sources with unwanted substances that continuously harm the environment.
- Air Pollution- Contamination of air due to smoke, fumes, pollen grains etc.
- Water Pollution- Water contaminated by sewage, industrial waste, excreta, chemicals, fertilizers etc.
- Soil Pollution- Soil gets contaminated or polluted with fertilizers, pesticides, garbage, chemicals etc.
Bio-geo-chemical Cycles
Interaction between biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere and these components form a cycle or chain called the biogeochemical cycle.
Water Cycle
Water from various sources evaporates, condenses and again precipitates as rain, hail, snowfall, sleet, falls on the land, flows back in the sea and the river is known as the water cycle. Through this cycle, the water is constant on the earth.

Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen from the atmosphere is fixed by the process of nitrification. Nitrification is done by nitrogen-fixing bacteria e.g. Rhizobium present in the soil helps the plants by making compounds of nitrogen that are absorbed by plants. The fixation is also done by the atmosphere or industries.
In the atmosphere, during lightning, high temperatures and pressures created in air convert nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen, which dissolves in water forming nitric and nitrous acids and is then used by life forms.
Plants contain nitrogen in the form of proteins or other complex compounds. Plants are eaten by animals. When dying bacteria present in soil act on and convert plants and animals various compounds of nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites.
Another group of bacteria convert these nitrates and nitrites into free, elemental nitrogen, this process is called denitrification.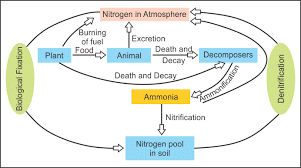
Carbon Cycle
Carbon is present in the compound form in the atmosphere ie., CO2, carbonates in water which forms limestone.
CO2 is taken by plants during photosynthesis to form organic compounds like glucose, carbohydrates, these plants are further eaten by animals, and decomposition gives CO2 back to the atmosphere.
Plants and animals get buried under the earth and do not decompose from coal and petroleum respectively. Animals and plants also release CO2 back into the atmosphere during respiration.
NCERT Solutions For Natural Resources Class 9 Biology
Q1. How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars?
Our atmosphere contains a mixture of many gases like nitrogen (78.08%), oxygen (20.95%), carbon dioxide (0.03%) and water vapour (in varying proportions). Whereas the atmosphere on Venus and Mars is mainly carbon dioxide.
This carbon dioxide constitutes up to 95-97% of the atmosphere on Venus and Mars. It is supposed that due to this reason no life is known to exist on these planets.
Q2. How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
As we know air is a bad conductor of heat and atmosphere and the average temperature of the earth keeps on increasing. The atmosphere prevents the sudden increase of temperature during day and night and escapes into outer space.
Q3. What causes winds?
Winds are caused due to unequal heating of the atmospheric air. This can be seen near the coastal areas. During the daytime, the air above the land gets heated very fast. As the air rises, low-pressure forms at the lower region. The movement of air from one region to another is wind.
Q4. How are clouds formed?
The water evaporates due to the heating up Of water bodies and other biological activities. The air also heats and rises.
On rising, it expands and cools to form tiny droplets. These droplets grow bigger, expand and form clouds. The collection Of dust and other suspended particles facilitate the process.
Q5. List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Human activities that would lead to air pollution
- Excessive use and burning of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum produce different oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. These are very harmful to our respiratory system and are also responsible for acid rain.
- Incomplete combustion of various fuels forms unburnt carbon particles which lower the visibility, especially in cold weather when water also condenses Out of air. This is known as smog and is a visible indication Of air pollution.
- Large usage Of automobiles and improper tuning of engines leads to the formation of carbon monoxide gas and Other oxides of nitrogen which causes a lot of respiratory problems.
- Forest fires, excessive mining and ore refining, excessive use of chlorofluorocarbons and excessive industrialisation lead to air pollution.
Q6. Why do organisms need water?
Organisms need water due for the following
- To carry out their life processes.
- The reactions that take place in our body need water as the medium to carry out the reactions within the cells.
- Substances are also transported from one part of the body to the other in a dissolved form.
- Water makes up about 70% of the bodyweight Of all living organisms. It also helps to maintain the temperature of our bodies.
- It helps in the digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients in the blood. Hence, organisms need to maintain the level of water within their bodies to stay alive. It helps in maintaining body temperature.
Q7. How is soil formed?
Soil is formed over a long period of time and takes millions of years to form as just a few centimetres of thick soil.
It starts from wearing away rocks at parent places and then the material erodes to form certain structures with the help of many agents of nature to help this way.
- The Sun: It causes heating of rocks which causes cracking and ultimately breaking up into smaller pieces.
- Water: It breaks rocks both by freezing and fast flow.
- Wind: It causes erosion of rocks similar to as done by fast-flowing water. It also carries sand from one place to the other as water does.
- Living organisms: Lichens and moss plants grow on the rock surface and cause the rock surface to powder down and form a thin layer of soil.
- The roots of big trees sometimes go into cracks in the rocks and as the roots grow bigger, the crack is forced bigger.
Q8. What is soil erosion?
The removal of the top layer of the soil along with all the nutrients and the organic-rich layer that is humus by the action of wind, water, sun, heat or action of glaciers. It may wash away the nutrient-rich layer and erode the rocks. This all would lead to loss of top layer and valuable resources.
Q9. What are the methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion?
The methods of preventing soil erosion are :
(i) Afforestation- forests are planted or re-planted to reduce the chances of soil erosion. It helps to fix the plants firmly to the ground to hold them tightly.
(ii) Shelterbelts- Trees planted in lines or hedges around farmland reduce erosion by reducing the speed of the wind.
(iii) Contour ploughing- Farmers make furrows across the sloping areas and it helps to hold water and does not allow it to flow down.
(iv) Terrace (or step) farming- A terraced hillside is less likely to be eroded than a natural hillside. Here a series of steps formed by horizontal strips supported by walls, catch the descending water. It gives the water sufficient time to percolate into the soil and nourish the crop.
(v) Soil cover– Soil left bare after harvesting a crop is often covered with dried vegetation to prevent erosion. Steep slopes that cannot be ploughed are covered with grass or pasture crops.
(vi) Preventing overgrazing- As the grass tends to bind soil molecules, even a very little grass on a field prevents soil erosion. But if the grass is overgrazed, it exposes the soil to erosion.
Q10. What are the different states in which water is found during the water cycle?
All three different states of water can be seen during the water cycle. These states are :
- Gaseous state (In the form Of water vapour which evaporates from the surface water).
- Liquid state (It is formed by the condensation of water vapour and can be Seen in the form of rain).
- A solid-state (It is formed by the freezing Of liquid droplets in the upper layer of the atmosphere which can be seen in the form Of snow, hail Or sleet).
Q11. Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Q12. List any three humans Who would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of the air.
Three human activities which would lead to an increase in the C02 content of air are :
Respiration- through a natural process both plants and animals exhale carbon dioxide and this is not very dangerous and does not have any adverse effect on the environment.
Combustion of fuels- The various types of fuels are burnt to provide energy for various needs like heating, cooking, transportation and industrial fuels.
Deforestation – Trees help in the conversion Of C02 into organic compounds such as glucose, starch, etc., by the process of photosynthesis. When these trees are cut non-judiciously, then the level of C02 increases in our environment.
Q13. What is the greenhouse effect?
Some gases prevent the escape of heat from the Earth. An increase in the percentage Of such gases in the atmosphere would cause the average temperatures to increase worldwide and this is called the greenhouse effect.
Q14. What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Elemental oxygen is normally found in the form Of a diatomic molecule (02) in the lower regions Of the atmosphere to the extent of 21 %. It is a non-poisonous form Of oxygen.
But in the upper reaches Of the atmosphere (stratosphere), it occurs in the form of ozone, containing three atoms of oxygen and having the molecular formula 03. It is the poisonous form of oxygen.
Conclusion
We have penned down the short and detailed notes of the Natural Resources class 9 Science along with the Ncert solutions and important diagrams to help out the students.
Students would be able to get a clear idea about how to attempt questions in the papers. Biology has been made easy for the students as we have explained all the terms very easily and in a detailed manner.