We have shared in-depth notes from the Class 9th biology chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce to help the students to get the gist of the lesson How do organisms reproduce along with NCERT Solutions of Class 10th How Do Organisms Reproduce.
We have also shared the mind map of the lesson How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th Science Ncert to give the chapter crux at a glance so that the board-appearing candidates can remember the gist of the lesson at once and can remember the biology terms very easily.
We have also provided some important diagrams of how do organisms reproduce class 10th to support the answers as we all know that diagrams are very important and play a crucial role and these also support the answers and make a student’s copy representable.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th: Introduction
Reproduction
o Biological process by which a living organism produces offspring similar to itself.
o Not essential for survival, but helps in the perpetuation of species.
o Information is transferred from the parents to the offspring in the form of DNA.
o DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)- a genetic material found in chromosomes present in the
nucleus of the cell.
o Two types of reproduction-sexual and asexual.
Sexual reproduction
o Requires two parents.
o Involves fusion of male and female gametes.
o Allows more variations in offspring.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th Sexual Reproduction
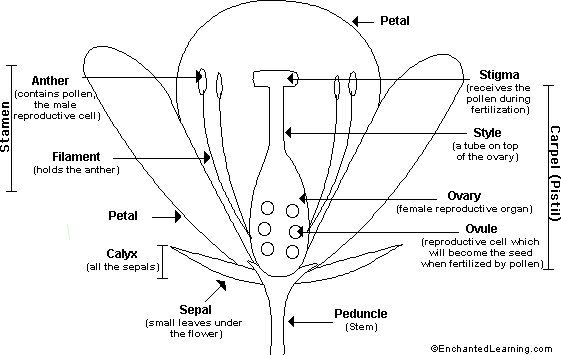
Angiosperms- flowering plants
o Flower is the reproductive part of angiosperms.
o Four parts of flowers– sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels/pistils
o Sepals- green in color, protect flower buds, collectively called calyx
o Petals- colorful structures, help in attracting pollinators, collectively called a corolla
o Stamens- male reproductive parts of flowers, consists of anther and filament
o Carpels- female reproductive parts of flowers, consists of style, stigma, and ovary
o Bisexual flowers– both stamens and carpels are present e.g. Hibiscus
o Unisexual flowers- either stamens or carpels are present e.g. corn
o Pollen or male gamete is released from the bursting of anther.
o Each ovule contains one egg cell or female gamete.
o Pollination- transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of the same or different flower.
o Fertilization- a fusion of male and female gametes
o After fertilization- the zygote forms the embryo, the ovule forms the seed, and the ovary forms fruit.
Sexual reproduction in humans
o Development into an adult or reaching maturity is essential for reproduction. The period of life, where changes set in for the development of a young individual into an adult, is
called puberty.
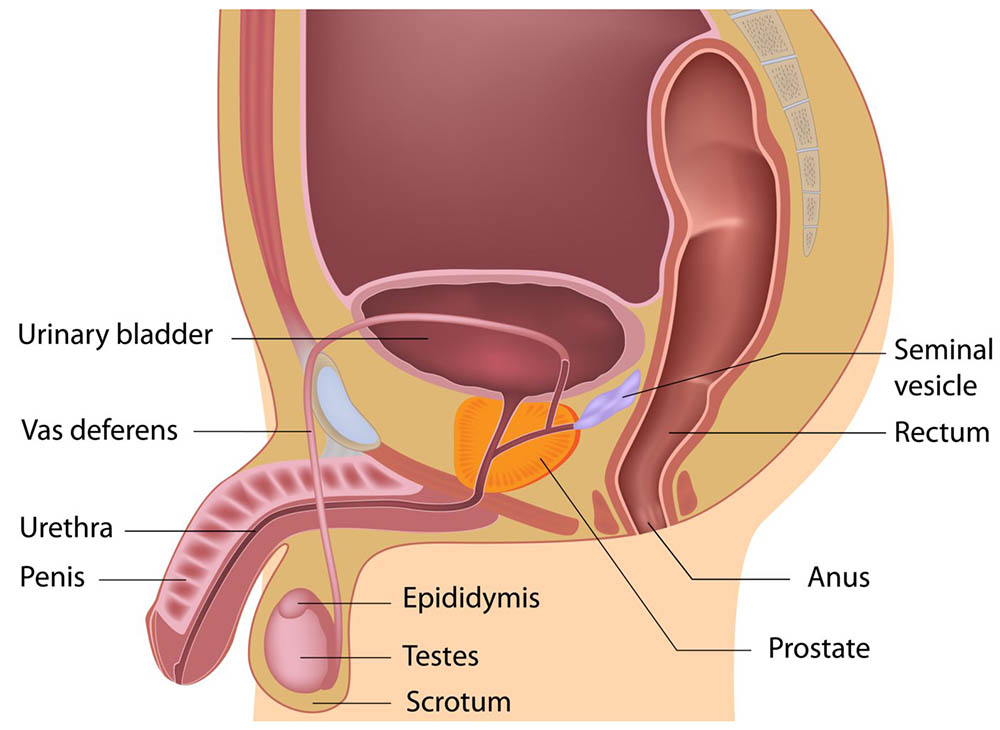
Male Reproductive System
o Male reproductive organs- pair of testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles
o Testes- produce sperms, testosterone
o Sperms- male gametes
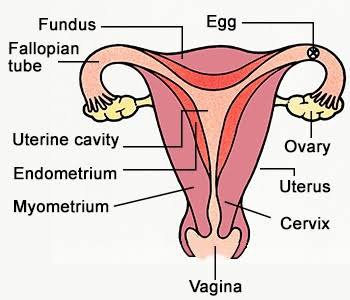
Female reproductive System
o Female reproductive organs- pair of ovaries, pair of oviducts, uterus, and vagina
o Ovaries contain thousands of eggs
o Sperms enter the female body through the vagina
Menstruation- if the egg is not fertilized, then the uterus lining breaks down and is
released in the form of blood and mucous through the vagina. It usually lasts for 2 to 8
days.
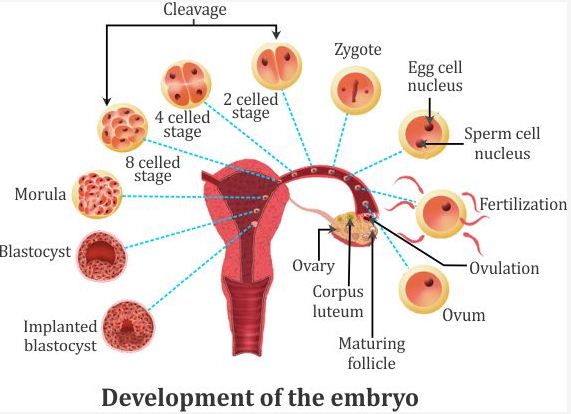
Development of the embryo
o The zygote repeatedly divides to form a ball of cells.
o The ball of cells then starts differentiating into tissues and organs. At this stage, it is
called embryo.
o Embryo gets attached to the wall of the uterus and develops various body parts such as
hands and legs.
o Foetus is a stage of an embryo that shows a main recognizable feature of a mature organism.
o Foetus develops for nine months inside the mother’s womb and is finally delivered.
o Fertilization- the fusion of the nucleus of the sperm with the ovum to form a zygote. It occurs in the fallopian tube of females.
o Zygote divides to form an embryo. The embryo is implanted in the uterus.
o Foetus develops inside the mother’s body for nine months (gestation period).
Vegetative propagation-in plants
New plants are formed from vegetative parts like roots, stems, and leaves. e.g. Bryophyllum propagates vegetatively by leaf buds.
Natural Methods of Vegetative Propagation
Stem propagation – The surface of the potato has several buds called eyes that develop into
new plants.
Propagation by leaf – The leaves of Bryophyllum has several buds at their margins that
develop into tiny plants.
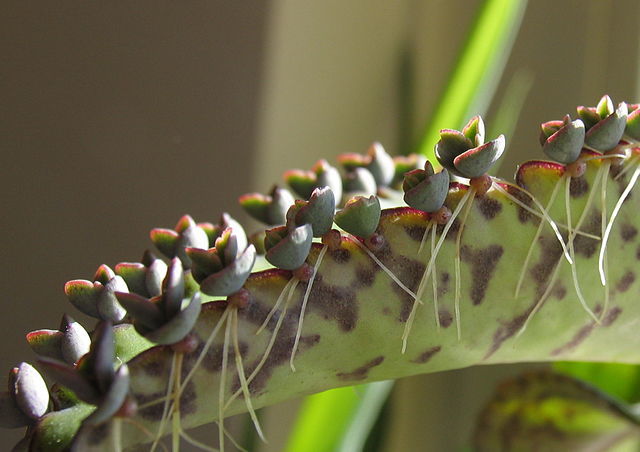

Propagation by roots – The roots of sweet potato, and dahlia get detached from the parent plant and give rise to a new plant.
Sugarcane, rose, money plant, etc. reproduce by stem cutting.
Advantages of vegetative propagation
Method of propagation for seedless plants such as sugarcane, potato, rose, etc.
Exact copies of the parent plant are produced.
Large numbers of offspring are produced.
Disease-free plants can be propagated.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th: Artificial Methods of Vegetative Propagation
Cutting – The artificial methods of vegetative propagation are
Stem cutting – Short lengths of the plant to be propagated are cut and planted in soil and they develop adventitious roots, and leaves grow into individual plants.
Eg. – Rose, Coleus, and Begonia are propagated by this method.
Root Cutting – In some plants, cutting roots are placed in soil and they develop into
individual plants. Eg. – Lime, Tamarind.
Layering – It consists of two methods they are
Mound layering – In this method, branches of plants to be propagated are bent to touch
the soil and the bent portion is covered by soil and roots grow at this node.
Air layering – Used for plants having thick stems. In these plants a part of the stem is
removed and is covered with moist cotton and enclosed in a bag, when roots appear after
some time, the branch is cut off and planted. Eg. – Rubber.
Grafting – In this method, two individual plants are used to derive a new plant. The plant
whose root portion is used is called stock and the plant whose stem portion is used is called the scion. The grafted end of the stock and the scion are cut obliquely and placed one upon the other. This is bound tightly. Grafting may be done in two ways they are
Bud grafting – the scion of a dormant bud is grafted onto a stock.
Eg. – Rose
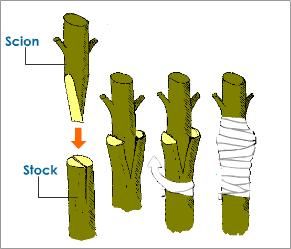
Stem grafting – It is usually done on closely related plants. In this method, either the stock is cut or slit where the scion is inserted and bound tightly.
Eg. – Mango, citrus, apple, etc.
Micropropagation or tissue culture – In this method, usually the meristematic tissue is
grown in a suitable medium and developed into a callus and then the callus is propagated
into a new plant.
Hybridization – In this method, the mating of two individuals of different genotypes is carried out. The new individual thus formed is called a hybrid.
The process involves
Selection of male and female parents.
The female flower is emasculated (anthers are removed).
Emasculation is followed by bagging (to prevent cross-pollination).
Pollen from the male plant is dusted onto the stigma of the female plant.
This method is used to get better varieties of crop plants.
Advantages of Hybridization
1. Higher yielding, better quality seeds are produced.
2. Disease and drought-resistant varieties can be developed
3. Adaptations to a wider range of habitats and
4. Insect and pest resistance.
Asexual reproduction
Does not involve the fusion of gametes.
Requires only one parent.
Offsprings produced are the exact copies of their parents.
Modes of asexual reproduction
Fission- involves cell division or splitting of cells e.g., Amoeba
Multiple fission: In multiple fission, a single cell divides into many daughter cells
simultaneously. Examples: Plasmodium and Amoeba
Fragmentation- new organisms formed from fragments of parents e.g., lichens
Regeneration- new organisms formed from body parts e.g., Planaria, Hydra
Budding- new individuals from protrusion called buds e.g., Hydra
Sexually transmitted diseases- infections that get transferred through sexual contact e.g., herpes, HIV-AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhea, etc.
Contraceptive methods to avoid pregnancy
o natural methods- abstinence
o barrier methods- condoms
o oral contraceptives- hormonal drugs
o implants- loop or copper-T
o surgical methods- Vasectomy and tubectomy
How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th: Mind Maps
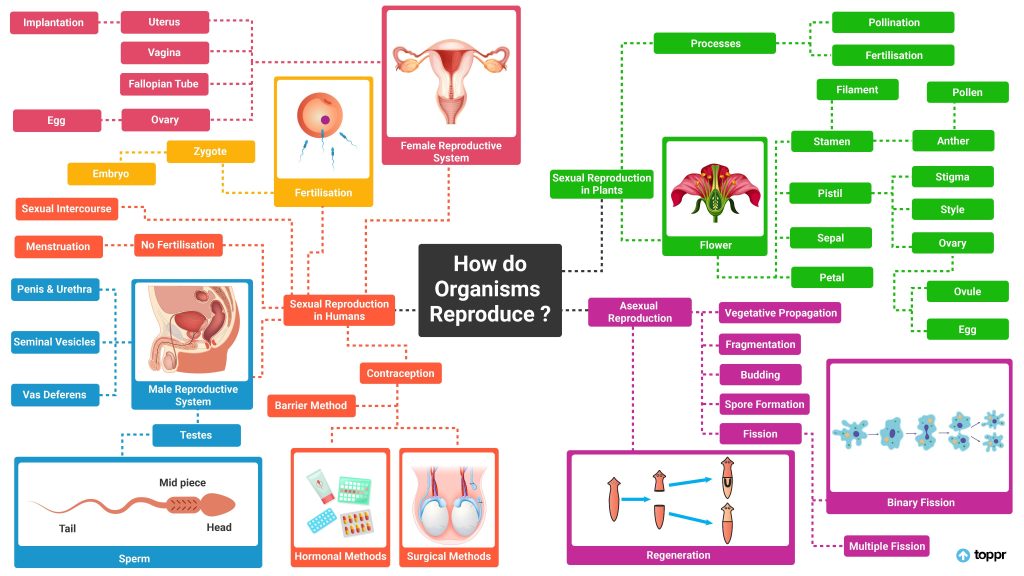
NCERT Solutions of Class 10th How Do Organisms Reproduce
Q1. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are
present in the nucleus of a cell. DNA is the information site for making proteins and
each specific type of protein leads to a specific type of body design.
Thus, it is the DNA molecule that determines the body design of an individual. Therefore,
it can be concluded that it is the DNA that gets transferred from parents to offspring and
makes them look similar.
Q2. Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Variations are more beneficial to the species than individuals because sometimes for a species, the environmental conditions change so drastically that their survival becomes difficult.
For example, if the temperature of water increases suddenly, then most of the bacteria
living in that water would die. Only a few variants that are resistant to heat would be able
to survive. However, if these variants were not there, then the entire species of bacteria
would have been destroyed.
Thus, these variants help in the survival of the species. However, all variations are not
necessarily beneficial for individual organisms.
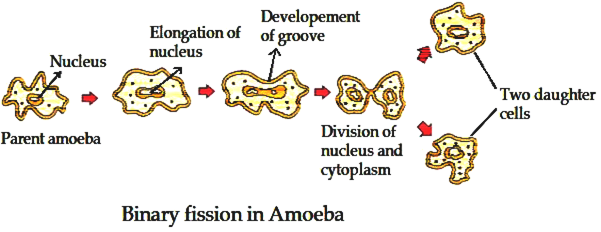
Q3. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
In binary fission, a single cell divides into two equal halves. Amoeba and Bacteria divide
by binary fission.
In multiple fission, a single cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously. Amoeba
and Plasmodium divides by multiple fission.
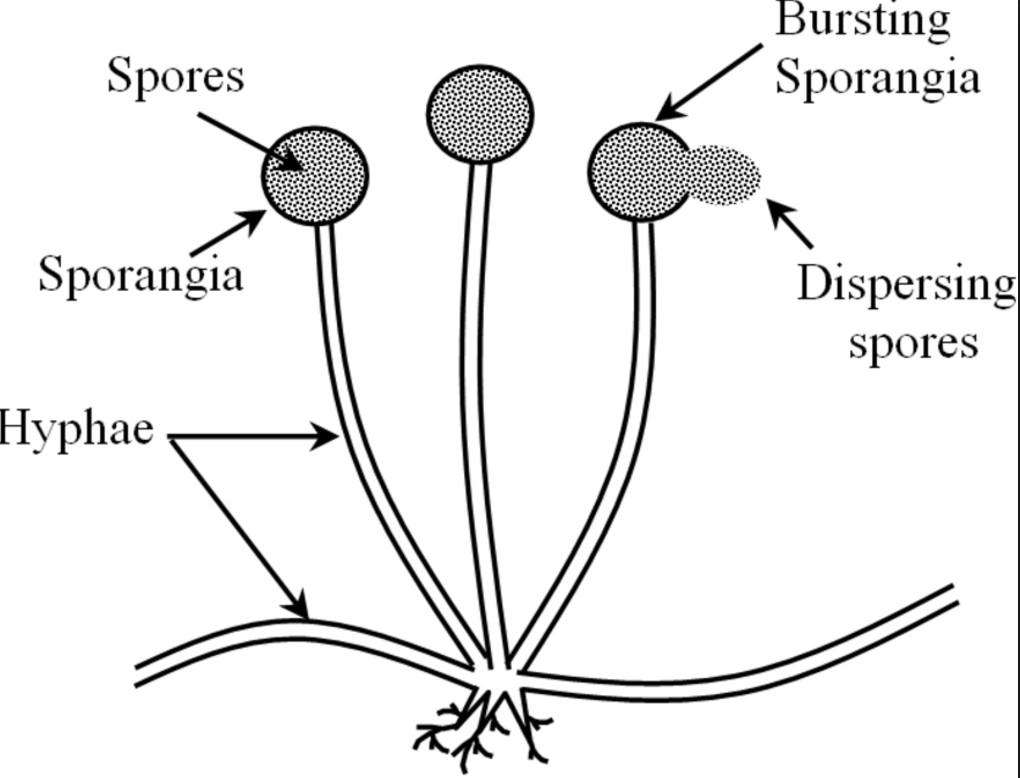
Q4. How will an organism benefit if it reproduces through spores?
There are many advantages if an organism reproduces through spores.
Advantages of spore formation:
Large numbers of spores are produced in one sporangium.
Spores are distributed easily by air to far-off places to avoid competition in one
place.
Spores are covered by thick walls to prevent dehydration under unfavorable
conditions.
Q5. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
(d) Cytokinin is a plant hormone.
Q6. How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Pollination is the process of transfer of pollens from anther to stigma. It occurs with the
help of certain pollinators such as air, water, birds, or some insects.
Fertilization, on the other hand, is the fusion of the male and female gametes. It occurs
inside the ovule and leads to the formation of a zygote.
Q7. What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Secondary sexual characteristics in girls:
• Increase in breast size and darkening of the skin of the nipples present at the tips of
the breasts.
• Appearance of hair in the genital area.
• Appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
• Increase in the size of the uterus and ovary.
• Beginning of menstrual cycle.
• More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
Q8. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
The embryo develops inside the mother’s body for about nine months. Inside the uterus,
the outer tissue surrounding the embryo develops finger-like projections called villi. These
villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood.
They provide a large surface area for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients. Also, there is a special tissue called the placenta, which is embedded in the uterine wall. The embryo receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood via the placenta. The waste materials produced by the embryo are also removed through the placenta.
Q9. Why does menstruation occur?
Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flow out every month through the
vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg.
Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilized, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
Q10. What are the different methods of contraception?
The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting sperms and ovum.
In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to the 17th of the menstrual
cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances
of fertilization are very high.
Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of the ovum and sperm is prevented
with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females.
Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover the penis in males
and the vagina in females.
Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These
contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus
fertilization cannot occur.
Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or
Copper-T is placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods can
also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens
to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, the fallopian tubes
of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as
tubectomy.
Conclusion
We have shared all about from the Class 9th biology chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce to help the students to get the gist of the lesson How do organisms reproduce along with NCERT Solutions of Class 10th How Do Organisms Reproduce.
We have also shared the mind map of the lesson How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10th Science Ncert to give the chapter crux at a glance so that the board-appearing candidates can remember the gist of the lesson at once and can remember the biology terms very easily.
Related Articles

