We have shared in-depth notes on Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10th to help the board-appearing candidates with the chapter. We have also shared NCERT Solutions for class 10th Globalisation And The Indian Economy to help them understand the lesson.
We also share the mind map of Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10th to make the students understand the lesson better and give them the gist.
Globalization And The Indian Economy Class 10th: Introduction
PRODUCTION ACROSS COUNTRIES
1. Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was primarily organized within
countries.
2. Colonies such as India export raw materials and foodstuff and import finished
goods.
3. Trade was the primary channel connecting distant countries. This was done before large companies called multinational corporations (MNCs) emerged on the scene.
4. An MNC is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation.
5. MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get cheap
labor and other resources.
6. MNCs are not only selling their finished products globally, but, more importantly, the goods and services are produced globally.
7. As a result, production is organized in increasingly complex ways.
INTERLINKING PRODUCTION ACROSS COUNTRIES
1. In general, MNCs set up production where it is close to the markets; where skilled and unskilled labor is available at low costs; and where the availability of other production factories is assured.
2. The money spent to buy assets such as land, building, machines, and other
equipment is called investment. The investment made by the MNCs is called foreign
investment.
3. The benefit to the local company of such joint production is two-fold.
(i) MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
(ii) MNCs might bring with them the latest technology for production.
4. But the most common way for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and expand production.
5. Many of the top MNCs have wealth exceeding the entire budget of the developing country’s government.
6. We see that there are various ways the MNCs spread their production and interact with local producers in various countries across the globe.
7. MNCs exert a strong influence on production at these distant locations.
8. As a result, production in these widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
FOREIGN TRADE AND INTEGRATION OF MARKETS
1. Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic
markets i.e., markets of their own countries.
2. For the buyers, importing goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
3. With the opening of trade, goods travel from one market to another.
4. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
WHAT IS GLOBALISATION?
1. A large part of the foreign trade is also controlled by MNCs.
2. A result of more significant foreign trade has been greater
integration of production and markets across countries.
3. Globalization is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
4. MNCs play a significant role in the globalization process.
5. More goods, services, investments, and technology are moving between
countries.
FACTORIES THAT HAVE ENABLED GLOBALISATION
1. Rapid technological improvement has been a significant factor that has stimulated globalization.
2. For instance, the past 50 years have seen several improvements in transportation
technology.
3. The development of information and communication technology has even more remarkable.
4. Technology in telecommunications, computers, and the internet has rapidly changed.
Liberalization of foreign trade and foreign investment policy
1. Tax on imports is an example of a trade barrier. It is called a barrier because some
the restriction has been set up.
2. The government can use trade barriers to increase or decrease foreign trade and to decide what kind of goods and how much of each should come into the country.
3. The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign investment.
4. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign
competition.
5. Barriers to foreign trade and investment were removed to a large extent.
6. This meant that goods could be imported and exported easily, and also foreign companies
could set up factories and offices here.
7. Removing barriers or restrictions the government sets is known as liberalization.
8. The government imposes much less restriction than before and is therefore said to be
more liberal.
Globalization And The Indian Economy Class 10th: World Trade Organization
1. We have seen that some very powerful international organizations supported the liberalization of foreign trade and investment in India.
2. These organizations say that all barriers to foreign trade and investment are harmful.
There should be no barriers.
3. World Trade Organization (WTO) is one such organization whose aim is to liberalize
international trade.
4. Though WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all, in practice, it is seen that the
developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers.
5. Conversely, WTO rules have forced developing countries to remove trade
barriers.
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION IN INDIA
1. In the last twenty years, the globalization of the Indian economy has come a long way.
2. Globalization and greater competition among local and foreign producers have benefited consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas.
3. As a result, these people today enjoy much higher living standards than was possible
earlier.
4. MNCs have increased their investments in India over the past 20 years, which means
investing in India has benefited them.
5. Several top Indian companies have benefited from the increased
competition.
6. Globalization has enabled some prominent Indian companies to emerge as
multinationals!
7. Globalization has also created new opportunities for companies providing IT-related services.
THE STRUGGLE FOR A FAIR GLOBALISATION
1. People with education, skills, and wealth have made the best use of new opportunities.
2. Conversely, many people have not shared the benefits.
3. Fair globalization would create opportunities for all and ensure that globalization’s benefits are shared better.
4. The government can play a significant role in making this possible.
5. Its policies must protect the interests of the rich and the powerful, and all the people in the country.
6. It can support small producers to improve their performance until they become
strong enough to compete.
7. If necessary, the government can use trade and barriers.
8. In the past few years, massive campaigns and representatives by people’s organizations
have influenced essential decisions relating to trade and investments at the WTO.
9. This has demonstrated that people also can play an essential role in the struggle for fair globalization.
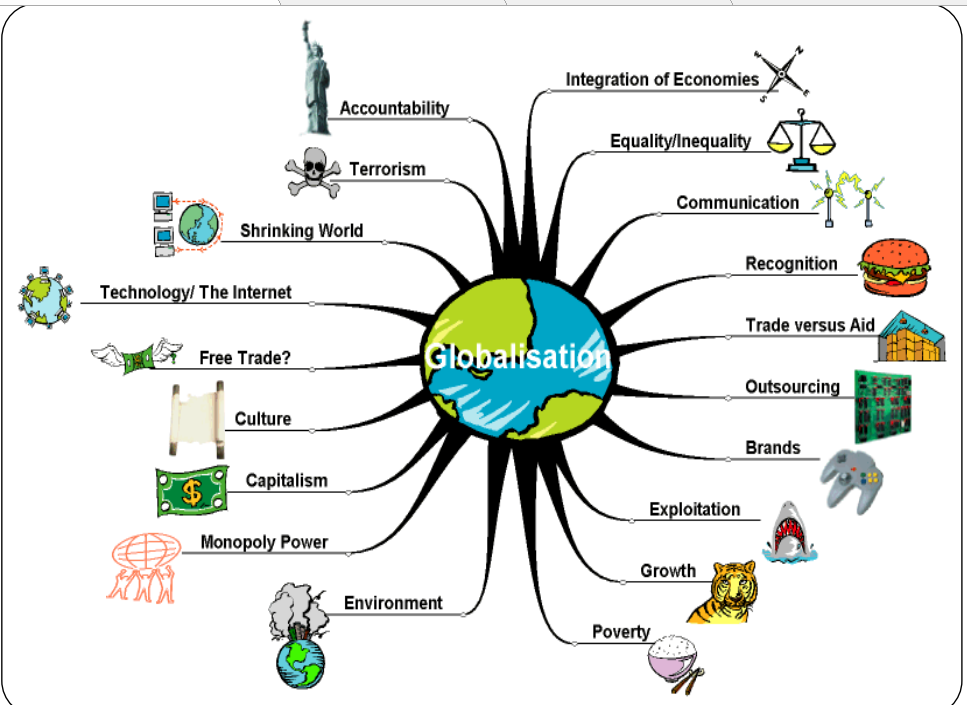
Globalization And The Indian Economy Class 10th: Mind Map
We have shared the mind map of Globalization And The Indian Economy in Class 10th to give the students of class 10th an opportunity for a conceptual understanding.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Globalization And The Indian Economy
We have shared some essential questions and answers related to NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Globalization And The Indian Economy to help the students get the lesson’s gist.
Q.1 What was the primary channel connecting countries in the past? How is it different now?
Trade was the primary channel connecting the countries in the past. For example, the Silk route connected different countries of the world; as a result, huge trade took place through this route. Trade in the past was restricted to finished goods produced in one market and sold in other markets.
In today’s time, trade, capital, technology, people, and services-flow are also taking place worldwide. Today the world is connected where production also occurs across different countries.
Q2. Distinguish between foreign trade and foreign investment.
Trade between two countries regarding goods and services is termed foreign trade. It helps in connecting the markets of different countries across the world. Foreign Investment made by an MNC or a financial institution either in the capital market or in the fixed assets in another country is termed foreign investment.
Q3. How will importing steel from India into the Chinese markets lead to the integration of markets for steel in the two countries?
Integration of markets for steel in the two countries will take place as follows
(a) Due to imports from India, choice in the Chinese market will increase.
(b) Steel producers in both countries will compete to get an increased market share.
(c) Prices of similar steel varieties in the Indian and Chinese markets will fluctuate and become equal after some time.
Q4. What is the role of MNCs in the globalization process?
Globalization is the rapid integration of the global economy through which countries can connect on various levels. Globalization has ensured development in trade and communication with different countries.
Over the last 20-30 years, MNCs have spearheaded a tremendous increase in globalization. MNCs are Multi-National Corporations or companies which have set up production in more than one country.
MNCs set up production in countries where they get possibilities of lucrative returns. Since the MNCs are producing and selling in many countries, they are interlinking the economies of these countries, thus speeding up globalization.
Q5. How is information technology connected with globalization? Would globalization have been possible without the expansion of IT?
Information technology has fastened the pace of globalization. It has revolutionized the way interaction is done. Owing to its development, people can instantly connect to anyone in every corner of the world.
Except for the physical movement of products, every other transaction is possible through the internet. Without it, Globalisation would have taken many more years to spread out, as the required information for taking any decision would have taken more time to be communicated and thus would have delayed the pace of integration among countries.
Q6. What do you understand by the liberalization of foreign trade?
Two restrictions on foreign trade (i.e., trade of goods and services between two sovereign nations) are removed by the liberalization of foreign trade.
(a) Entry Tax or Customs Duty: This is a mechanism whereby prices of imported goods are increased to provide leeway to domestic players. However, under liberalization, ideally, there will be no customs duty on any imported product.
(b) Lifting of Quotas or Restrictions on the Quantity being imported: This generally provides a cushion to domestic manufacturers from the cutthroat competition. However, under liberalization, there will be no restrictions on the number of goods, except in rare conditions, which would make the domestic firms face a higher level of competition.
Q7. How has competition benefitted people in India?
Competition from imported goods has benefitted people in India in the following ways
(a) Indian producers have improved their technology and quality to compete with foreign goods. (b) Prices of Indian goods have been reduced to match those of foreign goods, so buyers of these items have benefitted. (c) Some Indian companies have collaborated with foreign companies, and some MNCs have invested in Indian companies, thus benefiting both. There have been increased joint ventures between foreign and Indian companies, which have improved both business and created employment opportunities.
Q8. Why do governments try to attract more foreign investment?
Governments try to attract more foreign investment for the following reasons
(a) It provides necessary capital for undertaking economic activities, which would, in turn, boast GDP growth. (b) Leads to increased employment opportunities. (c) Provides the required tax income for the government.
Q9. How would flexibility in labor laws help companies?
The four essential factors for running a business/company are land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Against such a backdrop, if labor laws are flexible, it would mean- a less regulatory framework for recruiting or removing the labor, no strict working condition parameters, no underlying formal rules for working hours, and so on.
Since the objective of the business is profit maximization, such flexibilities ensure cost savings and thus lead to more significant profit and expansion of the company.
Q10. How do MNCs set up or control the production in other countries?
or
How are Multinational Corporations (MNCs) controlling and spreading their productions worldwide?
Multinational corporations (MNCs) usually set up their production units, where they find lucrative business conditions like– business-friendly government policies, economic skilled labor, proximity to the market, and so on.
In this regard, MNCs control products in the following ways Various ways in which MNCs control the production in other countries:
(i) Forging partnerships with local companies: By doing this, MNCs bring in the required capital and expertise in the running of a local company. In specific scenarios, the latest technologies are also shared, increasing the concerned business’s overall productivity. (ii) Competing with local companies or buying them up: MNCs often buy local companies or weed them out of business owing to their large capital base.
(iii) Outsourcing of required inputs: MNCs often use a local company’s products for making their product. E.g. in garments, footwear, sports items, etc. The products are supplied to MNCs with great power to determine price, quality, delivery, and labor conditions for these distant producers.
Q11. Why do developed countries want developing countries to liberalize their trade and investment? What do you think should the developing countries demand in return?
Developed countries want developing countries to liberalize their trade and investment for the following reasons:
- To make use of the untapped resource potential of developing countries.
- To ensure the utilization of the capital in some productive use which they have acquired throughout economic development.
However, in return, developing countries can negotiate for the following:
- Transfer of latest technology
- Least or zero environmental externalities.
- Adequate protection for vulnerable industries
- Humane treatment and condition of laborers.
Q12. How has liberalization of trade and investment policies helped the globalization process?
The easing of rules about trade and investment has led to an increased flow of investment and trade.
- It has promoted further integration among countries.
- Increased globalization has led to a more significant movement of people across borders.
Q13. How does foreign trade lead to the integration of markets across countries? Explain with an example other than those given here.
Increased trading activities among countries have strengthened markets in the following ways
- Foreign trade has led to increased producers’ competition, further increasing market efficiency.
- For the consumers, it has led to increased choices, which has led to increased consumer satisfaction.
- It has led to the availability of goods and services not previously available in the local market.
This is how markets are integrated through foreign trade. For example, Chinese electronic items are imported to India and have proved tough competition for less-technologically advanced companies.
Q14. Suppose you find two people arguing: One is saying globalization has hurt our country’s development. The other is telling that globalization is helping India develop. How would you respond to these arguments?
Both arguments have their share of truth. As Globalisation can be summed as having both positive and negative attributes. And these attributes can be stated as follow:
The positive impact of globalization on India (i) Greater variety of products, with improved quality and reasonable price.
(ii) Availability of products at an economical rate has led to a higher standard of living (iii) Increase in foreign direct investment (iv) Creation of employment in specific sectors. (v) Top Indian companies have benefited by investing in new technology and production methods and successful collaborations with foreign companies. (vi) This Has led to some prominent Indian companies emerging as multinationals. For example, Tata Motors, Infosys, Ranbaxy, etc. (vii) Created immense opportunities for companies in the service sector, particularly in IT.
The negative impact of globalization on India
(i) Producers who failed to compete, got perished. All this competition has led to increased unemployment. For instance, battery capacitors have been hit hard due to tough competition. (ii) This Has led to the greater casualization of work. Owing to increased pressure of competition, most employers prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’. This means that workers’ jobs are no longer secure.
Conclusion
We have shared Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10th Economics to help the class 10th students to be able to get their concepts clear regarding Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10th as it holds an essential value in the social science and students should know the positive and negative impacts of the Globalization.
Related Articles
- Drainage Class 9th NCERT Solutions Geography
- Nazism And The Rise Of Hitler Class 9 Social Science
- Socialism In Europe And The Russian Revolution Class 9 Social Science
- Constitutional Design: Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Civics Social Science Chapter 1: Power-sharing