We are sharing detailed notes of Atoms and molecules class 9th Science NCERT to help the students of class 9th with the chapter so that they can go through the chapter Atoms and molecules class 9th and better understand the lesson at a glance.
We are also sharing NCERT Solutions for class 9th Science chapter Atoms And Molecules to help the students of class 9th with the ncert solutions for class 9th science and boost their accuracy for the solutions.
Atoms And Molecules Class 9th Science: Introduction
Atoms
According to Dalton’s atomic theory
o Matter is made up of very tiny particles, and these particles are called atoms.
o Atoms cannot be divided further i.e., atoms are indivisible
o An atom can be defined as the smallest particle of matter that can neither be created nor destroyed by chemical means.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Law of conservation of mass
o Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It means that the sum of the masses of the reactants and the products remains the same during a reaction.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Law of constant proportion
o A chemical substance always contains the same elements in a fixed proportion by mass,
irrespective of the source of the compound.
The radius of the atom indicates the size of an atom, called the atomic radius. It is
often expressed in nanometers.
Representation of atoms
o The element’s symbol is made from one or two letters of the English or the Latin name of the element.
o Symbols are significant as they represent a particular element and one
atom of that element.
Atomic Mass
o The mass of an atom is known as the atomic mass.
o The atomic mass of an atom of an element is also known as its relative atomic mass since it is determined relative to the mass of the C-12 isotope.
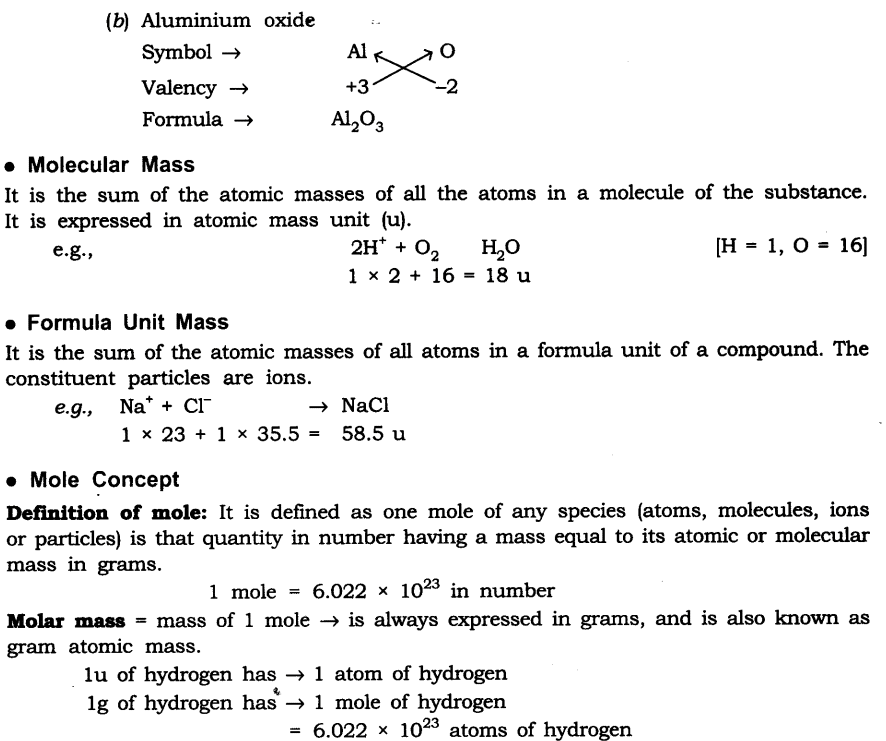
Gram molecular mass
The mass of one mole of atoms is known as the molar mass of
atoms, gram atomic mass, or gram atoms. For example, the atomic mass of nitrogen is 14
u and the gram atomic mass of nitrogen is 14 g. The mass of one-mole molecules of any substance equals the gram molecular mass of that substance.
Relative atomic mass or atomic weight is the ratio of the mass of one atom of an element to the mass of an atom of hydrogen taken as unity.
Gram molecular volume: The volume occupied by 1 gram molecule of dry gas at S.T.P is called gram molecular volume. The experimental value of 1 gram molecular volume of a gas is 22.4 L at S.T.P.
Molecule
o A molecule is formed when two or more atoms of the same or different elements combine chemically.
o The number of atoms that combine to form a molecule is called the atomicity of the
molecule.
Ion
o An ion is a charged species in which an atom or a group of atoms possess a net electric
charge (positive or negative).
o Positively charged ions are called cations (primary radical), and negatively charged
ions (acidic radicals) are called anions.
o Compounds in which molecules are formed by combining cations (positively
charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) are known as ionic compounds.
Chemical formula
o A chemical formula is the representation of the composition of a molecule in terms of the symbols of elements present in that molecule.
The molecular formula is a chemical formula that indicates the kinds of atoms and the
numbers of each kind of atom in a molecule of a compound.
To write the chemical formula of a compound, one should have prior knowledge of two
things.
o The symbols of the constituent elements.
o The combining capacity of the atom of each element constituting the compound.
Molecular Mass
o The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in a molecule of that substance.
Formula unit mass
o The formula unit mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms
present in a formula unit of that substance.
Mole Concept
o One mole of a substance is the quantity of the substance containing 6.022 × 1023 numbers of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). The number i.e., 6.022 × 1023 is the Avogadro number. It means that one mole of any substance (element or compound) contains 6.022 × 1023 particles (atoms of molecules).
o The mass of 1 mole of a substance is known as its molar mass.
Avogadro’s Law
Under the same temperature and pressure conditions, equal volumes of all gases contain an equal number of moles.
Gay-Lussac’s Law
At constant volume, the pressure of a fixed amount of a gas is directly
proportional to the temperature.
NCERT Solutions for class 9th Science chapter Atoms And Molecules
We provide NCERT Solutions for class 9th Science chapter Atoms And Molecules to help you with the solutions for Atoms And Molecules Class 9th Science NCERT to grasp the chapter and be accurate with the solutions.
Question 1. In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g of water, and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations agree with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Answer.

Question 2. Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Answer: The ratio of H: O by mass in water is:
Hydrogen: Oxygen —> H2O
∴ 1 : 8 = 3 : x
x = 8 x 3
x = 24 g
∴ 24 g of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas.
Question 3. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory results from the law of conservation of mass?
Answer: The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory that results from the law of conservation of mass is that the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Question 4. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Answer: The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Question 5. Define the atomic mass unit.
Answer: One atomic mass unit is equal to precisely one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found concerning an atom of carbon-12.
Question 6. Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Answer: Atom is too tiny to be seen with naked eyes. It is measured in nanometres.
1 m = 109 nm
Question 7. Write down the formulae of
(i) Sodium oxide
(ii) Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium sulfide
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide
Answer: The formulae are

Question 8. What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Answer: The compound’s chemical formula is a symbolic representation of its composition, e.g., the chemical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl.
Question 10. How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) P043- ion?
Answer: (i) H2S —> 3 atoms are present
(ii) P043- —> 5 atoms are present
Question 11. How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) P043- ion?
Answer: (i) H2S —> 3 atoms are present
(ii) P043- —> 5 atoms are present
Question 12. Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, C02, CH4, C2H2, NH3, and CH3OH.
Answer: The molecular masses are:
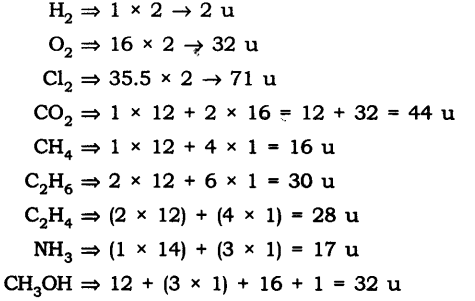
Question 13.Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2C03, given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
Answer: The formula unit mass of
(i) ZnO = 65 u + 16 u = 81 u
(ii) Na2O = (23 u x 2) + 16 u = 46 u + 16 u = 62 u
(iii) K2C03 = (39 u x 2) + 12 u + 16 u x 3
= 78 u + 12 u + 48 u = 138 u
Question 14. A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Answer: Boron and oxygen compound —> Boron + Oxygen
0.24 g —> 0.096 g + 0.144 g
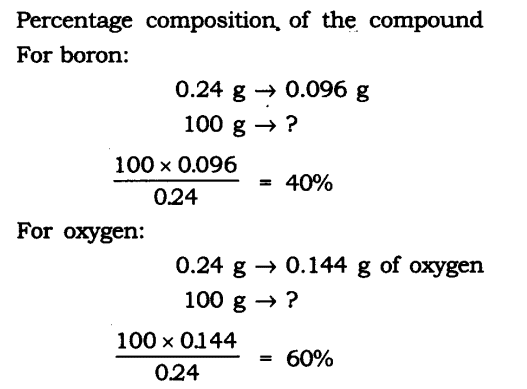
Question 15. When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
Answer: The reaction of the burning of carbon in oxygen may be written as:
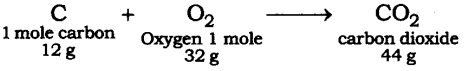
It shows that 12 g of carbon bums in 32 g of oxygen form 44 g of carbon dioxide. Therefore 3 g of carbon reacts with 8 g of oxygen to form 11 g of carbon dioxide. It is given that 3.0 g of carbon is burnt with 8 g of oxygen to produce 11.0 g of CO2. Consequently, 11.0 g of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.0 g of C is burnt in 50 g of oxygen, consuming 8 g of oxygen, leaving behind 50 – 8 = 42 g of O2. The answer governs the law of constant proportion.
Question 16. Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate.
Answer: (a) Magnesium chloride
Symbol —> Mg Cl
Change —> +2 -1
Formula —> MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide
Symbol —> Ca O
Charge —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaO
Question 17. Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulfate.
Answer: (a) Quick lime —> Calcium oxide
Elements —> Calcium and oxygen
(b) Hydrogen bromide
Elements —> Hydrogen and bromine
(c) Baking powder —> Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Elements —> Sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen
(d) Potassium sulfate
Elements —> Potassium, sulfur, and oxygen
Question 18. Calculate the molar mass of the following substances.
(a) Ethyne, C2H2
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 (Atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3
Answer: The molar mass of the following: [Unit is ‘g’]
(a) Ethyne, C2H2 = 2 x 12 + 2 x 1 = 24 + 2 = 26 g
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8 = 8 x 32 = 256 g
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4=4 x 31 = i24g
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl = 1 x 1 + 1 x 35.5 = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
(e) Nitric acid, HN03 = 1 x 1 + 1 x 14 + 3 x 16 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63 g
Question 19. What is the mass of
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b) 4 moles of aluminum atoms (Atomic mass of aluminum = 27)?
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulfite (Na2S03)?
Answer: (a) Mass of 1 mole of nitrogen atoms = 14 g
(b) 4 moles of aluminum atoms
Mass of 1 mole of aluminum atoms = 27 g
∴ Mass of 4 moles of aluminium atoms = 27 x 4 = 108 g
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulfite (Na2SO3)
Mass of 1 mole of Na2SO3 = 2 x 23 + 32 + 3 x 16 = 46 + 32 + 48 = 126 g
∴ Mass of 10 moles of Na2SO3 = 126 x 10 = 1260 g
Question 20. Convert into mole.
(a) 12 g of oxygen gas
(b) 20 g of water
(c) 22 g of Carbon dioxide.
Answer: (a) Given the mass of oxygen gas = 12 g
The molar mass of oxygen gas (O2) = 32 g
Mole of oxygen gas 12/32 = 0.375 mole
(b) Given the mass of water = 20 g
Molar mass of water (H2O) = (2 x 1) + 16 = 18 g
Mole of water = 20/18 = 1.12 mole
(c) Given mass of Carbon dioxide = 22 g
Molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2) = (1 x 12) + (2 x 16)
= 12 + 32 = 44 g
∴ Mole of carbon dioxide = 22/44 = 0.5 mole
Question 21. What is the mass of:
(a) 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms?
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules?
Answer: (a) Mole of Oxygen atoms = 0.2 mole
The molar mass of oxygen atoms = 16 g
Mass of oxygen atoms = 16 x 0.2 = 3.2 g
(b) Mole of water molecule = 0.5 mole
Molar mass of water molecules = 2 x 1 + 16= 18 g .
Mass of H2O = 18 x 0.5 = 9 g
Question 22. Calculate the number of sulfur molecules (S8) in 16 g of solid sulfur.
Answer: Molar mass of S8 sulphur = 256 g = 6.022 x 1023 molecule
Given the mass of sulfur = 16 g
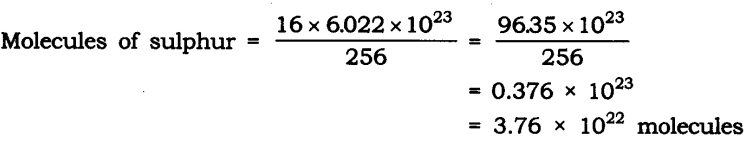
Question 23. Calculate the number of aluminum ions present in 0.051 g of aluminum oxide. (Hint: The mass of an ion is the same as that of an atom of the same element. The atomic mass of Al = 27 u)
Answer: Molar mass of aluminum oxide Al203
= (2 x 27) + (3 x 16)
= 54 + 48 = 102 g.

Conclusion
We have provided all about Atoms and molecules class 9th Science NCERT to help the students with the Class 9th Science chapter and better understand the NCERT Solutions For Class 9th Science chapter Atoms And Molecules.
Related Articles