We are providing you Geography class 9 chapter 1 India Size And Location with a brief explanation. These solutions and answers are beneficial among students of class 9 and they will help them to prepare thoroughly for the exams. All the answers related to chapter 1 geography class 9 will be given here and will help to tackle the doubts while solving the NCERT exercises.
India Size And Location Some key points
Topics in the chapter:
- India’s location
- It’s size
- India and the world
- Its neighbors
Introduction- India is one of the oldest civilizations having a remarkable history. Post-British rule, it has achieved much in the socio-economic sector. It has also made a remarkable achievement in the field of agriculture, industry, technology, and overall development.
India’s Location
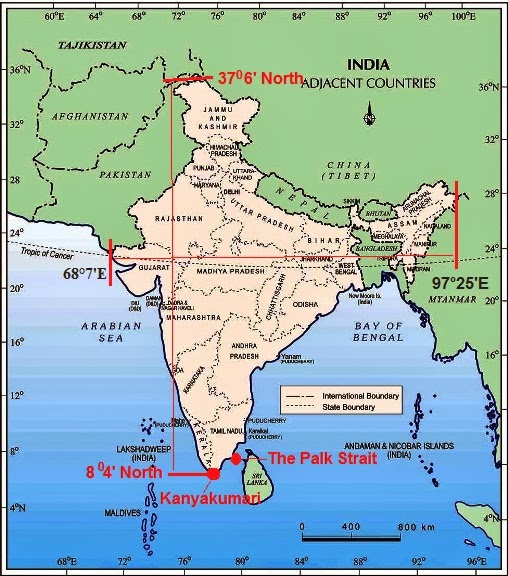
- Lies entirely in the Northern hemisphere between latitudes 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N and longitudes 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E.
- Divided by Tropic of cancer (23°30′ N) into almost two equal parts.
- In the Southeast, Andaman and Nicobar islands lie in the Bay of Bengal.
- In the Southwest, Lakshadweep islands lie in the Arabian Sea.
Its Size
- The total area of India is 3.28 million square km, which is 2.4 percent of the world’s total area.
- It is the seventh-largest country in the world in terms of landmass.
- It has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coastline of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands is 7,516.6 km.
- In the northwest, north, and northeast of India, young folds mountains bind it.
- South of about 22° north latitude, India narrows and finally extends towards the Indian Ocean. It also divides it into two seas, the Arabian Sea on the west and the Bay of Bengal on its east.
- The latitudinal and longitudinal extent of the mainland is about 30°.
- India’s east-west extent appears to be smaller than the north-south extent.
- The time along the Standard Meridian (82°30′ E) passing through Mirzapur in UP is taken as the Indian Standard Time for the whole country.
- The time gap between Arunachal Pradesh present in the east and Gujarat present in the west is about 2 hours. The latitudinal extent influences the duration of day and night, as one moves from south to north.
India and the World
- India is located in the center of the World between East and West Asia.
- The routes across the Indian ocean which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India.
- The Deccan Peninsula* helps India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
- The Ocean which is south of India given the name the Indian Ocean as no other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has.
- The land routes of India are much older than sea routes. Various passes across mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travelers as the ocean limited such interaction for a long time.
- The land routes helped India in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times.
- India has propagated the ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals, and the decimal system, and given spices, muslin, and other merchandise to different countries.
- Also, the influence of Greek sculpture and the architectural styles of domes and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of India.
Its neighbors
- India is comprised of 29 states and 7 union territories and shares its land boundary with:
- Northwest: Pakistan and Afghanistan
- North: China, Nepal, Bhutan
- East: Myanmar and Bangladesh
- South: Sri Lanka and the Maldives
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar
- Maldives Islands are situated to the south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
- A peninsula is a piece of land bordered by water on three sides but connected to the mainland.
India Size And Location Class 9 Map
Here’s a political map of India.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Chapter 1
Q1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through
(a) Rajasthan (b) Odisha
(c) Chhattisgarh (d) Tripura
(ii) The easternmost longitude of India is
(a) 97° 25′ E (b) 68° 7′ E
(c) 77° 6′ E (d) 82° 32′ E
(iii) Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim have common frontiers with
(a) China (b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal (d) Myanmar
(iv) If you intend to visit Kavaratti during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territories of India you will be going to
(a) Puducherry (b) Lakshadweep
(c) Andaman and Nicobar (d) Daman and Diu
(v) My friend hails from a country that does not share land boundaries with India. Identify the country.
(a) Bhutan (b) Tajikistan
(c) Bangladesh (d) Nepal
Answers
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through – (b) Odisha.
(ii) The easternmost longitude of India is – (a) 97° 25′ E.
(iii) Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim have common frontiers with (c) Nepal.
(iv) Kavaratti is situated at the union territories of (b) Lakshadweep
(v)(b) Tajikistan does not share a land boundary with India.
Q2.
- Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea?
- Name the countries which are larger than India?
- Which island group of India lies to its southeast?
- Which island countries are our southern neighbors?
Answers
- Lakshadweep islands.
- Russia, Canada, the USA, China, Brazil, and Australia.
- Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- Srilanka and Maldives
Q2. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
There is a time lag of two hours from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh but because of the standard meridian of India (82degree 30’E) which passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh. Because India has adopted the same standard time, so all the watches will show the same time in Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh as well as in other parts of the country.
Q3. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
The Trans-Indian ocean route which connects Europe to East Asia proves to be a strategic central location. The Deccan peninsula also outflows into the Indian Ocean and thus it helps to establish close contacts with Europe, Africa, and West Asia. India also enjoys the fact that there is no other country that has a long coastline on the Indian ocean and so it justifies the name of an ocean as India Ocean.
Conclusion
We have provided ncert solutions for class 9 geography chapter 1 in brief and detailed explanation. We have also included some key facts of India Size And Location for the students to go through before their examinations and along with that we have provided you all with the important map to be able to deal with the map skills work.

