Here in this article, we are sharing the notes of Manufacturing Industries Class 10th NCERT to help the students with the lesson so that they could attempt maximum questions of this chapter.
We are also sharing Manufacturing Industries Class 10th map work, important diagrams, and NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Manufacturing Industries to help the board-appearing candidates in every possible way.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: Introduction
Manufacturing:-
Production of goods in large quantities by processing raw materials into more valuable products is called manufacturing. Manufacturing industries are known as secondary activities, as these industries manufacture primary materials (like cotton) into
finished goods (like textiles)
Importance of Manufacturing:-
Manufacturing industries help in modernizing agriculture; which forms the
the backbone of our economy.
Manufacturing industries also reduce the heavy dependence on agricultural
income because of the creation of new jobs in secondary and tertiary
sectors.
Industrial development helps in the eradication of unemployment and poverty.
Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce which helps to bring in much-needed foreign exchange. A country with a high level of manufacturing activities becomes prosperous.
Agriculture and Industries:-
Agriculture and industries depend upon each other. On one hand, many industries like sugar, textile, etc depend on agricultural products, cotton is the raw material in cotton textile mills.
On the other hand, many industrial products like fertilizers, irrigation pumps, PVC pipes, tractors, machines, and tools help in increasing agricultural productivity.
The share of the manufacturing sector in the GDP (Gross Domestic Product) has stagnated at 17% over the last two decades. The total contribution of industry to the GDP is 27% out of which 10% comes from mining, quarrying, electricity, and gas.
The growth of the manufacturing sector had been 7% in the last decade. Since 2003, the growth rate has been 9 to 10% per annum. The desired growth rate over the next decade is 12%.
The National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) has been set up with the objectives of improving productivity through proper policy interventions by the government and renewed efforts by the industry.
National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC):-
It has been set up by the Government of India to provide a continuing forum for policy dialogue to energize and sustain the growth of manufacturing industries in India.
Industrial Location:-
The location of an industry is influenced by Government policies,
availability of raw materials, labor, capital, power, and market facilities.
Factors that Affect the Industrial Location:-
Geographical factors:-
Availability of raw material.
Energy and power resources.
Suitable climate.
Land
Availability of water. (Inexpensive and abundant in case of some industries
like Jute)
Non-geographical factors:-
Contribution of Industry to National Economy:-
Labour
Capital
Bazaar/Markets’
Services like Transport, Communication, Banking, Insurance, etc.
Financial advice
Government policies
Infrastructure
Entrepreneur
Manufacturing Industry and Urbanisation:-
Industrialization and urbanization depend upon each other. Industries
are located around the cities where there are markets for industrial goods
and services like banking, insurance, transport, labor, consultants and
financial services are available.
During the pre-independence era manufacturing units were located near
the seaports for overseas trade such as Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai. Many
industries tend to come together to make use of advantages offered by
urban centers known as Agglomeration Economies.
Urbanization:- The increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities.
Agglomeration Economies :-
These occur when the larger market, lower transportation costs and
other benefits outweigh the added expenses (such as higher rent or taxes)
of working in a city.
Industry and market are closely linked with each other. A number of
factors/ components which link these, are:-
Money is needed to buy inputs for production. After selling the finished
products in the market manufacturers/ industrialists also gain profit in the
form of money. Inputs (like raw materials/component parts) are needed to produce goods in industries.
Land, labor, capital, entrepreneur, and infrastructure are the factory of production. A good network of transport is needed to supply raw materials from the source regions to factories and finished products to markets. Factories are set up to produce different product outputs. After manufacturing the finished goods a well-developed market is needed to sell these goods.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: Classification of Industries
Industries are classified on the basis of the following criteria:-
Classification of industries on the basis of raw materials:-
Agro-Based Industries :- Cotton, woollen, jute, silk textile, rubber,
sugar, tea, coffee, etc.
Mineral-Based Industries:- Iron and steel, cement, aluminum,
petrochemicals, etc.
Classification of industries according to their main role:-
Basic or Key Industries:- These industries supply their products or raw
materials to manufacture other goods, for Example:- iron and steel, copper
smelting, aluminum smelting.
Consumer Industries:- These industries produce goods that are
directly used by consumers, for Example:- sugar, paper, electronics, soap,
Classification of industries on the basis of capital investment:-
Small Scale Industry:- If the invested capital is up to ₹1 crore, then the
the industry is called a Small Scale Industry.
Large Scale Industry:- If the invested capital is than ₹1 then the
the industry is called Large Scale Industry.
Classification of industries on the basis of ownership:-
Public Sector:- These industries are owned and operated by
government agencies, for Example:- SAIL, BHEL, ONGC, etc.
Private Sector:- These industries are owned and operated by
individuals or a group of individuals, for Example:- TISCO, Reliance,
Mahindra, etc.
Joint Sector:- These industries are jointly owned by the government
and individuals or a group of individuals, Example:- Oil India Limited.
Cooperative Sector:- These industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers, or both. The resources are pooled by each shareholder and profits or losses are shared proportionately. AMUL which is Milk Cooperative is a good example. The Sugar Industry in Maharashtra is another example.
Classification of industries on the basis of bulk and weight of raw
materials and finished goods:-
Heavy industries:- in which large machines and heavy or bulky raw
materials are used to produce products, including capital goods like
automobiles and construction machinery. For example:- Iron and steel
industry.
Light Industries:- in which light raw materials are used to produce
light utility goods, Example:- electrical industries, toy industry.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: Types of Industries on the Basis of Material Used
On the basis of materials used the industries are classified into:-
Agro-based industries
Mineral-based industries.
Agro-Based Industries:-
Industries based on agricultural raw materials are called agro-based
industries. Examples are cotton textiles, jute textiles, woolen textiles, silk
textiles, synthetic textiles, the sugar industry, etc.
Types of Agro-Based Industries
Textile Industry
The textile industry contributes 14% to industrial production in India. 35 million people are directly employed in the textiles industry in India. In terms of employment generation, this industry is the second largest after agriculture.
It earns approximately 24.6% of the foreign exchange. The contribution of the textile industry to GDP is 4%. This is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain.
Cotton Textile
The first successful cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
Mahatma Gandhi laid emphasis on the spinning of yarn and wearing khadi
so that weavers could get employment. In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton-growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujrat.
Availability of raw material, market, transport facilities ( port ), labor, and moist climate contributed to its localization.
While spinning continues to be centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamilnadu, weaving is highly decentralized to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and design of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc. Cotton goods are exported to Japan, the USA, the UK, Russia, France, East European countries, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and several African countries.
Problems before the cotton industry in India:-
Old and traditional techniques.
Low output of labor.
Stiff competition with the synthetic fiber industry.
Erratic power supply.
Lack of new machinery and need for up-gradation especially in weaving and
processing sectors.
Jute Textiles
India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods. The first jute mill was set up near Kolkata in 1859 at Rishra. It stands second in the jute export after Bangladesh. After the partition in 1947, the jute mills remained in India, but three-fourths of the jute-producing area went to Bangladesh (erstwhile East Pakistan). The jute industry is located along the Hugli river in West Bengal.
The factors responsible for the location of jute mills in the Hugli basin are
West Bengal is the largest producer of Jute in India. Abundant and inexpensive water from the Hugli river for processing raw jute. Cheap labor from West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Uttar Pradesh. Supported by a good network of railways, roadways, and waterways to
facilitate the movement of raw material to the mills.
Inexpensive (Cheap) water transport and Kolkata port for the export of jute
goods. Being a large urban center Kolkata provides banking, insurance, and other
facilities.
Challenges faced by the Jute industry
Things from synthetic fiber are on the market.
Synthetic fiber is cheap, compare to jute.
Jute cultivation is very expensive and hard.
Stiff competition in the international market from other substitutes is a big
challenge.
Bangladesh is a big challenge as a competitor while Brazil, the Philippines, Egypt
and Thailand is another competitor.
Sugar Industry
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies first place
in the production of gur and Khansari. Sugar mills in India spread over Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Gujarat. In recent years, there is a tendency for the mills to concentrate in the Southern and Western states, especially in Maharashtra. This is because the cane produced here has a higher sucrose content and a cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season.
Challenges faced by the Sugar industry
1. This is a seasonal and short-term industry.
2. Sugarcane production per hectare is low.
3. Old machines in use.
4. Inefficient method of production.
5. Need to maximize the use of baggage.
6. Transport delay in reaching cane to factories.
Mineral Based Industries
Industries that use minerals and metals as raw materials are called
mineral-based industries.
Iron and Steel Industry
The iron and steel Industry is the basic industry since all the other industries- heavy, medium, and light depend on it for their machinery. India ranked second in the production of crude steel in the world with 111 million tonnes in 2019.
India is the largest producer of sponge iron. But its per capita consumption was only 74.3 kg per annum in 2019 against 229.3 kg of the world average. Most public sector undertakings market their steel through the Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL).
Chotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of Iron and Steel industries.
Due to the maximum concentration of iron and steel industry in the
Chotanagpur plateau region-
Low cost of iron ore.
High-grade raw materials in proximity.
Available Cheap labor.
Vast growth potential in the domestic market.
Process of manufacturing of steel-
Process of manufacturing steel, iron ore, coking coal, and limestone are
needed in the ratio of approx. 4 : 2: 1. Manganese is also required to harden
the steel.
The processes of manufacture of steel are shown below
Transport of raw material to plant (Iron-ore, coking coal, limestone,
manganese)
Blast Furnace:- Iron ore is melted. Limestone is fluxing material that is added. The slag is removed. Coke is burnt to heat the ore.
Pig Iron:- Molten materials are poured into molds called pigs.
Steel Making:- Pig iron is further purified by melting and oxidizing
the impurities. Manganese, nickel, and chromium are added.
Shaping Metal:- Roling, pressing, casting, and forging
Reasons why the iron and steel industry is called basic industry:-
Many other industries are dependent on the iron and steel industry.
The iron and steel industry provides machines to other industries such as sugar
industry or cement industry etc.
The industrial progress of the country depends on this industry.
Provide jobs to a large number of people.
Reasons why the iron and steel industry is called heavy industry:-
All the raw materials, like iron ore, coal and lime are heavy in nature.
Finished products of this industry need a high cost of transport.
Due to the lack of full development of the iron and steel industry in India
The challenges due to which India is not able to perform to its full
potential in this industry are:-
Processes
Limited availability and high cost of coking coal.
Poor infrastructure
Lower labor productivity.
Irregular supply of energy
Aluminum Smelting:-
It is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
Bauxite is the basic raw material of this industry which is a very bulky, dark
reddish-colored rock.
Aluminum is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of heat,
malleable and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
It is used to manufacture aircraft, utensils, and wires.
Aluminum has gained popularity as a substitute for steel, copper, zinc, and
lead in different industries.
The factors responsible for the location of this Industry are a regular supply
of electricity and availability of raw materials at minimum cost.
In India, aluminum smelting plants are located in Odisha, West Bengal,
Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
Chemical Industries:-
In India, the chemical industry is fast growing and diversifying in nature. It comprises both large and small-scale manufacturing units. The chemical industry has two sectors namely organic and inorganic sectors.
Organic sector
The organic sector produces organic chemicals. These chemicals include
petrochemicals. Petrochemicals are used for the manufacturing of synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, plastics, dyestuff, drugs, and pharmaceuticals.
Organic chemical plants are located near oil refineries or petrochemical
plants.
Inorganic sector
The inorganic sector produces inorganic chemicals. These chemicals include sulphuric acid used to manufacture fertilizers, synthetic fibers, plastics, adhesives, paints, dyes pieces of stuff, nitric acid, alkalies, soda ash (used to make glass, soaps, and detergents paper), and caustic soda. These chemical plants are located all over the country.
Fertilizer Industry
The fertilizer industries are centered around the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (mainly urea) and complex fertilizers which have a combination of nitrogen (N), phosphate (P), and potash (K). Potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potassium compounds.
After the Green Revolution, the industry expanded to several parts of the country. Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Kerala contribute towards half of the fertilizer production.
Cement Industry
Cement is essential for construction activities such as building houses, factories, bridges, roads, airports, dams, and for other commercial establishments. This industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, and gypsum. The first cement plant was set up in Chennai in 1904.
After independence, the industry flourished in India. Its plants are located in Gujarat due to its access to the market in the gulf countries.
Why the development of the Cement industry is very important for our
country?
Our cement industry provides the best quality product. There is a great demand in Asian and African countries and within India also. This industry is doing well in production and export. Decontrol of price and distribution since 1989 and other policy reforms led
the cement industry to make rapid strides in capacity, process, technology, and production.
Automobile Industry
Automobiles provide vehicles for quick transportation of goods and passengers. After the liberalization, the coming of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market. The industry is located around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, etc.
How the liberalization and direct foreign investment have made a
rapid growth in the automobile industry of India?
The coming of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market after the liberalization. It led to the healthy growth of the industry including passenger cars, and two and three-wheelers.
Foreign direct investment brought in new technology and aligned the industry with global developments. The industry had experienced a quantum jump in less than 15 years.
At present, there are 15 manufacturers of passenger cars,9 commercial
vehicles, and 14 of the two and three-wheelers.
It covers products from transistor sets to televisions, telephones, cellphones, telephone exchanges, radars, computers, and other equipment required by the telecommunication and computer industry.
Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other important centers for electronic goods are Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Pune, Delhi, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Coimbatore.
Contribution of India’s information and technology industry to the economic development
Provides employment.
Has been a major foreign exchange earner.
The number of working women has increased.
The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the
the success of the IT industry in India.
Software technology parks provide single window service and high data
communication facility to software experts.
Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Although industries have contributed significantly to India’s economic growth and development their waste products have caused environmental degradation.
Industries are responsible for four types of pollution i.e. air, water, land
and noise.
Air pollution
It is caused by the presence of a high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries, and smelting plants, and the burning of fossil fuels leads to air pollution.
Information Technology (IT) and Electronics Industry
It adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings and the
the atmosphere as a whole.
Water pollution
It is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers. The industries which are mainly responsible for water pollution are
paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries, and electroplating industries.
Thermal pollution
Pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Noise pollution
It is the propagation of noise with a harmful impact on the activity of human or animal life. It results in irritation, anger, hearing impairment, and increased heart rate, and blood pressure.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: Control of Environmental Degradation
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th Some suggestions to minimize the industrial pollution of freshwater
Minimizing water usage by reusing and recycling wastewater in two or more successive stages. Rainwater harvesting to meet water requirements. Treating hot water and industrial wastes before releasing them into rivers and ponds.
This can be done in three phases:-
Primary treatment by mechanical means (i.e. screening, grinding,
flocculation and sedimentation.)
Secondary treatment by biological processes. Such as planting trees, rain
water harvesting.
Tertiary treatment by chemical, physical and biological processes like
recycling of wastewater, in sewage treatment plants.
General measures to minimize environmental pollution are:-
1. Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industries needs to be regulated
legally.
2. Generators and other machinery should be fitted with silencers and other
noise-absorbing materials to reduce their sound.
3. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to
factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and
inertial separators.
4. Use of oil or gas instead of coal to reduce smoke emissions from factories.
Redesigning of machinery to increase their efficiency in using energy.
5. Promote sustainable development by integrating economic development
goals with environmental construction.
NTPC:-
National Thermal Power Corporation is a major power-providing corporation in India. It has ISO certification 14001 for developing Environment Management Systems. A major task of NTPC is to set up power plants by conserving the natural environment and resources like air, water, oil gas, coal, and other fuels.
This is possible via:-
1. Optimum utilization of equipment, adopting the latest techniques, and upgrading old equipment wherever possible.
2. Minimizing waste generation in thermal power plants by adopting ash utilization techniques.
3. Development of green belts by afforestation to maintain ecological balance.
4. Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash
water recycling system, and liquid waste management.
5. Installing facilities for ecological monitoring, review, and online database
management in all the power stations.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: MCQs
We have also shared Manufacturing Industries Class 10th MCQs to help the students to get thorough with the lesson and get the crux of the chapter Manufacturing Industries Class 10th NCERT.
Question 1.
India occupies first place in the production of:
(a) Sugar
(b) Jute
(c) Gur and khandsari
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Gur and Khansari
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies first place in the production of gur and Khansari.
Question 2.
The number of sugar mills in the country is:
(a) 400
(b) 420
(c) 440
(d) 460
Answer
Answer: (d) 460
There are 460.
Question 3.
Industries that use minerals and metals as raw materials are called:
(a) Agro-based industries
(b) Metal-based industries
(c) Mineral-based industries
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Mineral-based industries
They are called mineral-based industries.
Question 4.
Which of the following is basic industry:
(а) Sugar
(b) Cotton
(c) Jute
(d) Iron and steel
Answer
Answer: (d) Iron and steel
The basic industry is the iron and steel industry.
Question 5.
Iron ore, coking coal, and limestone are required to make steel in the ratio of approximately:
(a) 1 : 2: 4
(b) 2 : 1: 4
(c) 4: 2: 1
(d) 4:1:2
Answer
Answer: (c) 4 : 2 : 1
They are required in the ratio of 4: 2: 1.
Question 6.
India ranks ……………………………. among the world’s crude steel producers.
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Ninth
(d) Tenth
Answer
Answer: (c) Ninth
India ranks ninth among the world’s crude steel producers.
Question 7.
In spite of the large quantity of production of steel, per capita consumption per annum is only:
(a) 20 kg
(b) 32 kg
(c) 40 kg
(d) 52 kg
Answer
Answer: (b) 32 kg
It is only 32 kg per annum.
Question 8.
In the 1950s China and India produced almost the same quantity of:
(a) Iron
(b) Manganese
(c) Copper
(d) Steel
Answer
Answer: (d) Steel
Both these countries produced the same amount of steel.
Question 9.
The number of aluminum smelting plants in India are:
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 14
Answer
Answer: (a) 8
There are eight aluminum smelting plants in India.
Question 10.
In 2004, India produced over 600 million tonnes of:
(a) Steel
(b) Aluminium
(c) Copper
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Aluminium
In 2004, India produced over 600 million tonnes of aluminum.
Question 11.
The chemical industry in India contributes approximately:
(а) 3 percent of the GDP
(b) 4 percent of the GDP
(c) 5 percent of the GDP
(d) 6 percent of the GDP
Answer
Answer: (а) 3 percent of the GDP
It contributes about 3 percent of the GDP.
Question 12.
The fertilizer industry is centered around the production of:
(а) organic fertilizers
(b) inorganic fertilizers
(c) nitrogenous fertilizers
(d) phosphate fertilizers
Answer
Answer: (c) Nitrogenous fertilizers
The fertilizer industry produces mostly nitrogenous fertilizer.
Question 13.
The industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, alumina, and gypsum are:
(а) Iron and steel industry
(b) Aluminium industry
(c) Cement industry
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Cement industry
The cement industry requires all the above raw materials.
Question 14.
The first cement plant was set up in Chennai in:
(a) 1804
(b) 1904
(c) 1814
(d) 1914
Answer: (b) 1904
It was set up in 1904.
Question 15.
At present the number of manufacturers of passenger cars and multi-utility vehicles is:
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) 20
Answer
Answer: (c) 15
There are 15.
Question 16.
The full form of BPO is:
(а) Business Progress Outstanding
(b) Business Processes Outstanding
(c) Business Processes Outsourcing
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Business Processes Outsourcing
The full form of BPO is Business Processes Outsourcing.
Question 17.
Production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to valuable products is called:
(а) Finishing
(b) Completing
(c) Manufacturing
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to valuable goods.
Question 18.
People employed in secondary activities manufacture the primary materials.
(а) Raw materials
(b) Complete goods
(c) Usable goods
(d) Finished goods
Answer
Answer: (d) Finished goods
People employed in secondary activities manufacture the primary materials into finished goods.
Question 19.
Export of manufactured goods expands:
(a) Only trade and commerce
(b) Brings in much-needed foreign exchange
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
The export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce and brings in much-needed foreign exchange.
Question 20.
Agriculture and industry are:
(a) Exclusive to each other
(b) Not exclusive to each other
(c) Not inter-related to each other
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Not-exclusive to each other
Agriculture and industry are not exclusive to each other.
Question 21.
The trend of growth rate in manufacturing over the last decade has been around:
(а) 7 percent per annum
(b) 8 percent per annum
(c) 9 percent per annum
(d) 10 percent per annum
Answer
Answer: (а) 7 percent per annum
It has been 7 percent per annum.
Question 22.
Industrial locations are influenced by:
(а) Availability of raw materials
(b) Labour and capital
(c) Power and market
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Industrial locations are influenced by all the above factors.
Question 23.
The full form of NMCC is:
(а) National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council
(b) National Manufacturing Country Council
(c) National Mass Counting Council
(d) No Manufacturing Competitive Council
Answer: (а) National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council
It refers to National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council.
Question 24.
Cotton, jute, silk, sugar, etc. are examples of:
(a) Textile industries
(b) Heavy industries
(c) Agro-based industries
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Agro-based industries
All are produced from agricultural products and are therefore known as agro-based industries.
Question 25.
The only industry in the country which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain is:
(a) Agro-based industry
(b) Heavy industry
(c) Textile industry
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Textile industry
The textile industry is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Manufacturing Industries
Q1. Explain the Reasons why the iron and steel industry is called the basic industry.
- Many other industries are dependent on the iron and steel industry.
- The iron and steel industry provides machines to other industries such as the sugar
industry or cement industry etc. - The industrial progress of the country depends on this industry.
- Provide jobs to a large number of people.
Q2. Explain the factors responsible for the location of jute mills in the Hugli basin.
West Bengal is the largest producer of Jute in India. Abundant and inexpensive water from the Hugli river for processing raw jute. Cheap labor from West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Uttar Pradesh. Supported by a good network of railways, roadways, and waterways to
facilitate the movement of raw material to the mills.
Inexpensive (Cheap) water transport and Kolkata port for the export of jute
goods. Being a large urban center Kolkata provides banking, insurance, and other
facilities.
Q3. What is the Contribution of India’s information and technology industry to economic development?
- Provides employment.
- Has been a major foreign exchange earner.
- The number of working women has increased.
- The continuing growth in hardware and software is the key to the
the success of the IT industry in India. - Software technology parks provide single window service and high data
communication facility to software experts.
Q4. Discuss the steps to be taken to minimize environmental degradation by industry.
Minimizing the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it, is done in two or more successive stages.
- Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
- Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them into rivers and ponds.
Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases:
- Primary treatment by mechanical means.
This involves screening, grinding, flocculation, and sedimentation. - Secondary treatment by biological process.
- Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical, and physical processes. This involves the recycling of wastewater.
General measures to minimize environmental pollution are:-
1. Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industries needs to be regulated
legally.
2. Generators and other machinery should be fitted with silencers and other
noise-absorbing materials to reduce their sound.
3. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to
factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and
inertial separators.
4. Use of oil or gas instead of coal to reduce smoke emissions from factories.
Redesigning of machinery to increase their efficiency in using energy.
5. Promote sustainable development by integrating economic development
goals with environmental construction.
Q5. How do industries pollute the environment?
Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Although industries have contributed significantly to India’s economic growth and development their waste products have caused environmental degradation.
Industries are responsible for four types of pollution i.e. air, water, land
and noise.
Air pollution
It is caused by the presence of a high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries, and smelting plants, and the burning of fossil fuels leads to air pollution.
Information Technology (IT) and Electronics Industry
It adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings and the
the atmosphere as a whole.
Water pollution
It is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers. The industries which are mainly responsible for water pollution are
paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries, and electroplating industries.
Thermal pollution
Pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Noise pollution
It is the propagation of noise with a harmful impact on the activity of human or animal life. It results in irritation, anger, hearing impairment, and increased heart rate, and blood pressure.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10th: Map Work
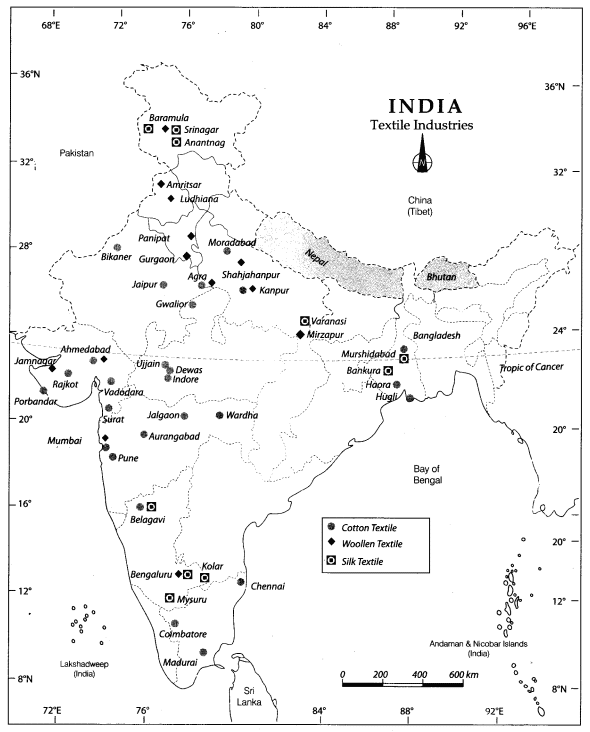
This map shows the cotton, woolen, and silk textile industries of India.
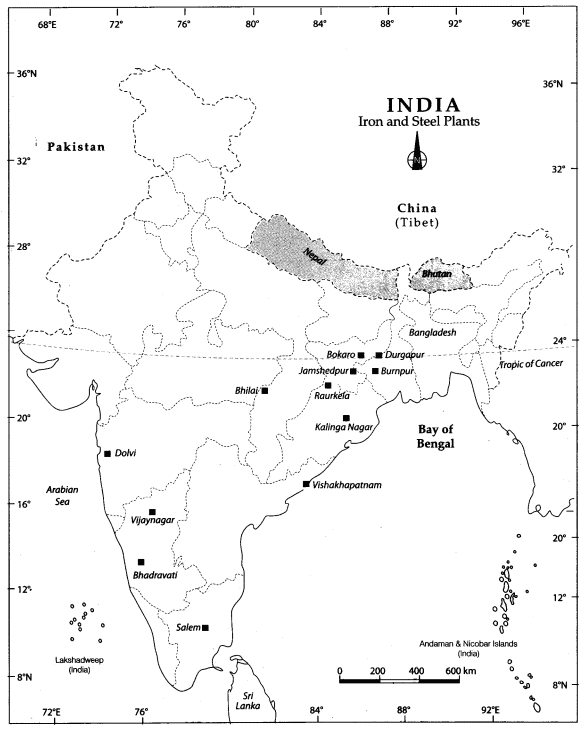
This map shows the Iron and Steel Plants of India. Iron and Steel is a heavy industries because all the raw materials, as well as finished goods, are heavy and bulky.
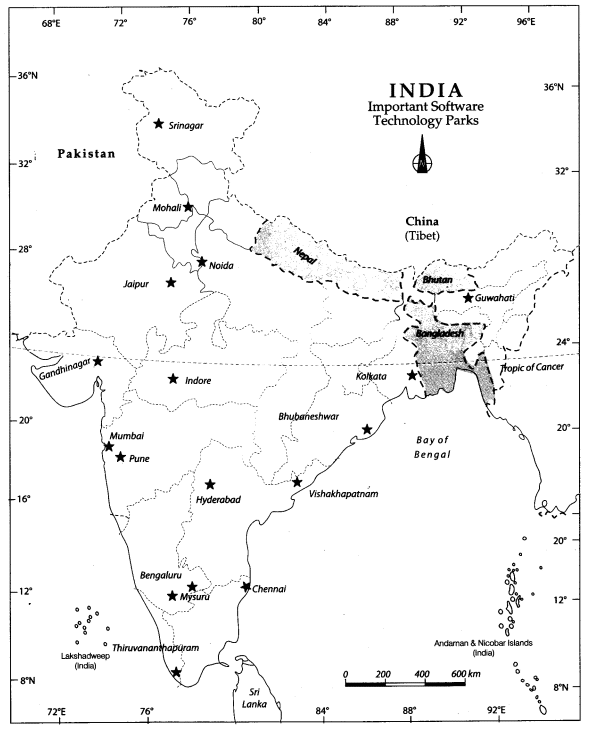
This map shows the software technology parks in India. Bengaluru is known as the electronic capital of India.
Question 1.
Locate and label the following items on the given map with appropriate symbols.
1. Silk industry – Mysuru, Kolar, and Srinagar
2. Cotton textile industry – Ahmedabad, Surat, and Kanpur
3. Woolen industry – Ludhiana, Panipat, and Amritsar
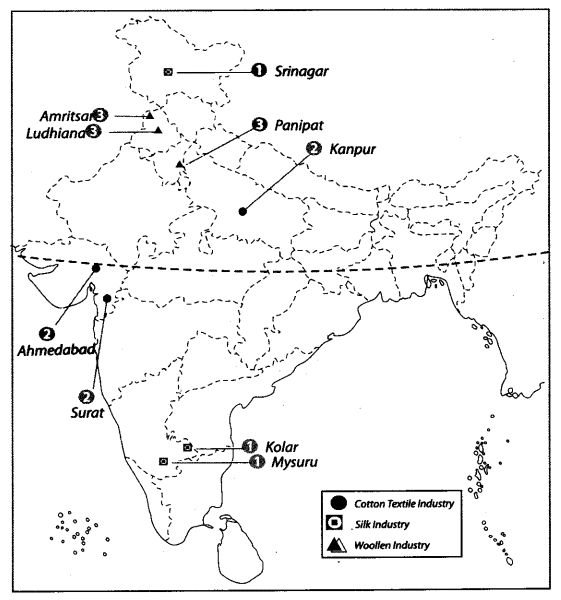
Question 2.
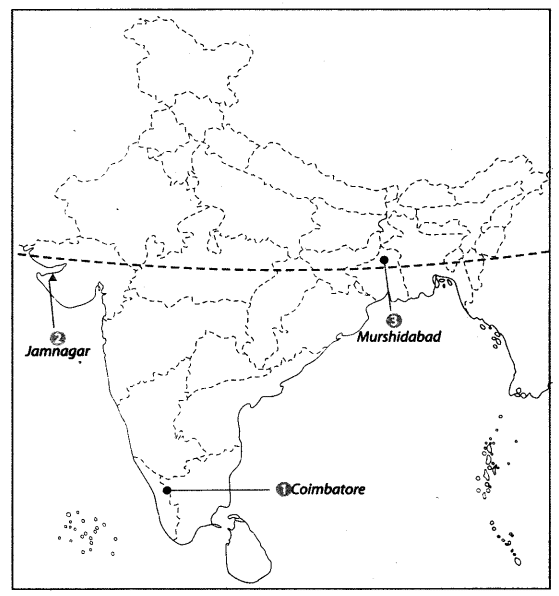
Features are marked by numbers in the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
1. Cotton textile industry
2. Woolen industry
3. Silk industry
Conclusion
We have penned down all about Manufacturing Industries Class 10th NCERT to help the students with the lesson so that they could attempt maximum questions of this chapter. We are also sharing Manufacturing Industries Class 10th map work, important diagrams, and NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Manufacturing Industries to help the board-appearing candidates in every possible way.

