We have shared Sources Of Energy Class 10th Science NCERT notes to help the students with the lesson along with we have also provided NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Science chapter Sources Of Energy.
We are also sharing some important diagrams of Sources Of Energy Class 10th to help the students with the crux of the lesson and be able to attempt the questions in the board examinations.
Sources Of Energy Class 10th: Introduction
Biomass refers to those living and nonliving organic materials that can be used as sources
of energy in the form of fuel. Some examples of biomass fuels are wood, crops, and organic garbage. Biomass fuel is a renewable source of energy. Gas made from the anaerobic digestion of agricultural and animal waste is called biogas.
Biodegradation is the process of biological degradation of organic matter by bacteria and
fungi.
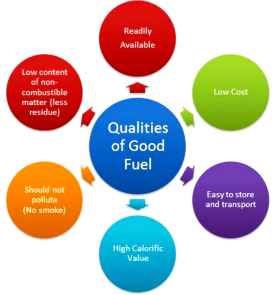
A good fuel/source of energy
o That would do a large amount of work per unit volume or mass
o Easily accessible
o Easy to store and transport
o Economical
Factors to be considered for choosing fuel
o How much heat it produces
o Less smoke generation
o Easy availability
Calorific value is defined as the amount of heat energy obtained by burning one gram of a substance. The unit of calorific value is kJ/g.
The ignition temperature of a substance is defined as the temperature at which the
substance starts burning. It is measured in °C, °F, or K.
Non-renewable sources of energy are those that are consumed at a rate faster than that at which they are replenished. Example: Fossil fuels.
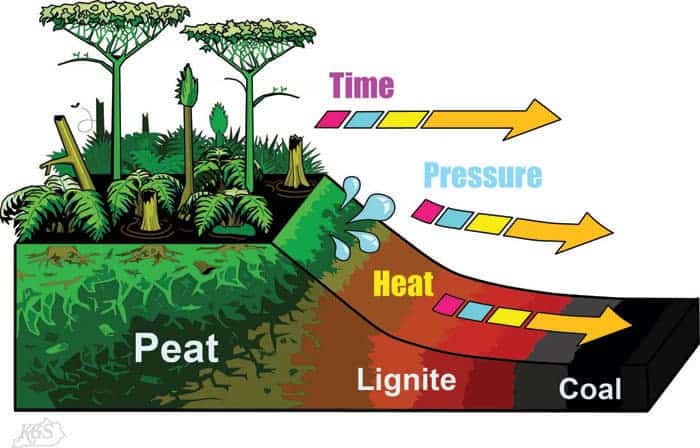
Fossil fuels – Coal, petroleum, and natural gas
o Coal: It is a non-renewable source of energy made up of complex compounds of carbon,
hydrogen and oxygen along with some free carbon and compounds of nitrogen and
sulfur.
o Petroleum: It is a dark-colored viscous liquid also known as crude oil or black gold. It is a complex mixture of many hydrocarbons with water, salt, earth particles, and other
compounds of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
We obtain petroleum by drilling oil wells into the earth’s crust at its reservoirs. The petroleum extracted from wells has to be purified to obtain different useful components. The process of separating useful components from crude oil is called refining and this process is done by fractional distillation in big refineries.
o Natural Gas
The main constituents of natural gas are methane (up to 95%), ethane, and propane. It easily burns to produce heat.
Advantages –
Easy availability
Generate heat that is easily converted into electricity
Renewable sources of energy are those that are replenished at a rate faster than that at
which they are consumed. Example:
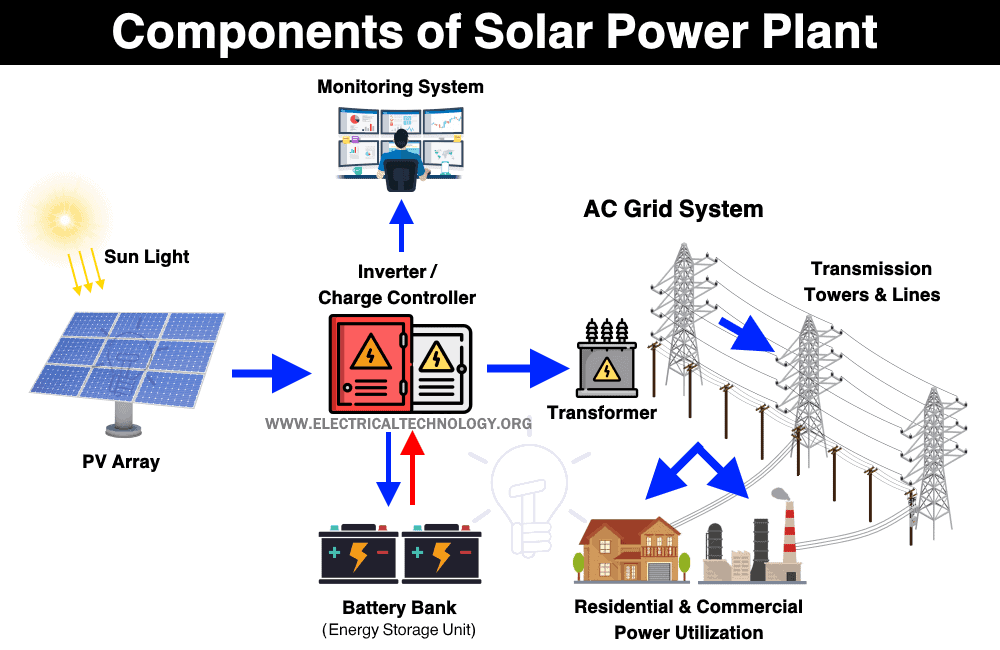
o Solar energy
Solar cooker, solar water heater (very efficient for small-scale electricity
production)
o Tidal energy, wave energy, ocean thermal energy
o Geothermal energy – Heat energy inside the earth
o Nuclear energy – Not dependent on solar energy, never-ending source, very efficient
source, more environmentally friendly.
Devices that use solar energy – Solar cooker, solar water heater, etc.
Photovoltaic cells or solar cells convert solar energy into electric energy.
Solar cooker helps in cooking food by converting solar energy into heat energy.
A solar water heater heats water using solar energy.
Advantages of solar energy:
o It is a renewable source of energy
o Solar radiations are abundantly available
o Solar cell panels have no moving parts and hence require little maintenance.
Disadvantages of solar energy:
o Photovoltaic cells are not cost-effective
o A typical cell develops a voltage of 0.5 to 1 V and can produce about 0.7 W of electricity
when exposed to the sun
o Availability of special grades of silicon used to produce solar cells is limited
Coal and petroleum
o They are non-renewable sources of energy.
o Consumption of coal and petroleum has increased in the past few years due to rapid
industrialization.
o Burning of coal and petroleum releases toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, sulfur
dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.
o Use of coal and petroleum can be reduced by using alternate sources of energy and
switching over to cleaner biofuels.
Sustainable Management
o Interests of all the stakeholders should be given a proper say.
o Benefits of development should reach each and every individual and all generations.
Thermal power plant – Coal and petroleum are burned to produce steam by heating
water to spin a turbine.
Thermal power plant – Nonrenewable source.
Hydropower plants use the potential energy of water accumulated at a height to spin a
turbine.
Hydropower plant – (Renewable source)
Problems – Limited places for construction (only Hilly areas)
Biomass refers to those living and nonliving organic materials that can be used as sources of energy in the form of fuel.
Some examples of biomass fuels are wood, crops, and organic garbage.
Biomass fuel is a renewable source of energy.
Gas made from the anaerobic digestion of agricultural and animal waste is called biogas.
Biodegradation is the process of biological degradation of organic matter by bacteria and
fungi.
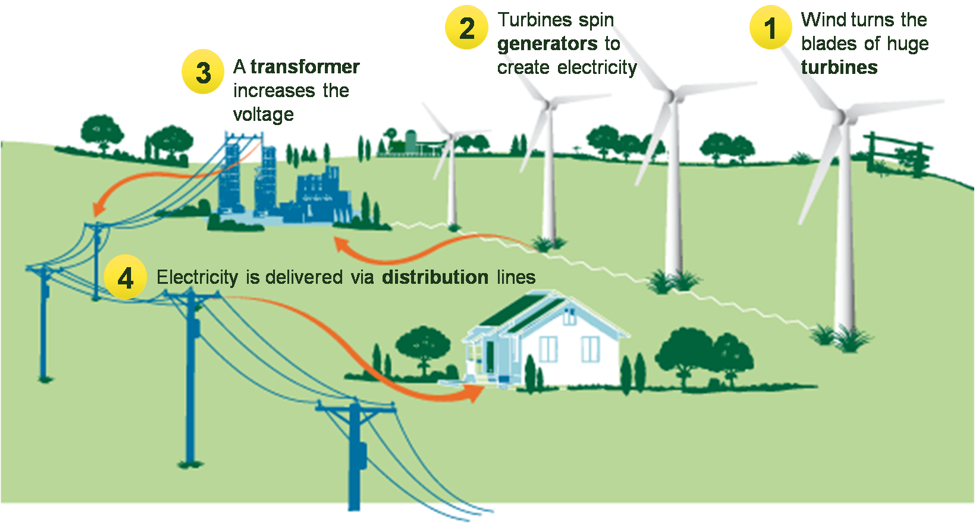
Wind energy is the energy harnessed from wind. The kinetic energy of wind is converted
into mechanical energy.
Windmill converts wind energy into mechanical energy used for grinding stone or
pumping water.
Advantages:
o Wind is freely available in nature
o Air is a renewable and inexhaustible source of energy
o It reduces the cost of electricity produced
o Wind energy does not cause any pollution and is eco-friendly
Limitations:
o Wind farms can be established only at places where there is a continuous wind speed of
over 10 mph
o A wind farm requires a large area (about 2 hectares) to facilitate a 1 MW generation
o Lack of energy storage facilities to provide energy backup in the absence of wind
o The initial cost of setting up a farm is quite high
Tidal Energy: Tides are the daily rise and fall of ocean levels relative to coastlines. They
are a result of the gravitational forces of the moon and the sun on Earth, and also the
revolution of the Earth. A large amount of energy is stored in tides. They can be used as
renewable sources of energy to generate electricity.
Wave energy: Ocean waves are caused by winds as they blow across the sea. Waves are a powerful source of energy. Electricity can also be produced from wave energy.
Ocean thermal energy: Sunlight falls on oceans and seas. This causes the temperature of the water on the surface to rise, while the temperature at the bottom remains comparatively cooler. Ocean thermal energy conversion plants use warm surface water to boil volatile liquids such as ammonia. Ammonia gas, thus produced, creates pressure and runs the turbine of the generator. This produces electricity. Cold water is pumped up to liquefy the gas. This creates a cycle for generating electricity.
Nuclear energy – Not dependent on solar energy, never-ending source, very efficient
source, more environmentally friendly.
Nuclear power plants consist of nuclear reactors. These reactors use uranium rods as fuel and heat are generated by the process of nuclear fission.
Disadvantages of nuclear energy:
o Construction of nuclear power plants needs huge investments
o Radioactive wastes such as used uranium are a dangerous hazard to the environment
o Nuclear energy can be used for negative purposes. Therefore, there is always a fear of
misuse
o There is always a danger of leakage of radioactive material and radiation from nuclear
power plants
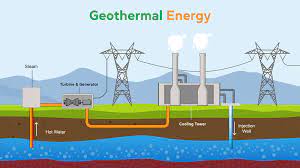
Geothermal energy – Heat energy inside the earth emerges due to the high temperature in the Earth’s interior.
Hot spot – Spot where hot rocks known as magma heats the underground water to
produce steam.
Hot spring – an outlet for the underground heated water to reach the Earth .
Applications:
For driving turbines or generators to produce electricity
To heat buildings
Advantages:
Fuel not required
Energy is almost free
Absence of polluting emissions
No role in the greenhouse effect
Geothermal power stations are small
Minimal adverse impact on the environment
Disadvantages:
Commercially non-feasible
Hot spots are sparse
Hazardous gases may emerge which are difficult to dispose
Geothermal sites may deplete and lose their heat.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Science chapter Sources Of Energy
Question 1:
What is a good source of energy?
Answer 1:
A good source of energy should have the following qualities:
It should be easily available.
It should do a large amount of work (or produce a large amount of heat) per
unit volume/mass.
It should be easy to store and transport.
It should be economical.
It should cause less environmental pollution.
Question 2:
What is good fuel?
Answer 2:
A good fuel produces a large amount of heat on burning but does not produce a lot
of smoke and is easily available.
Question 3:
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Answer 3:
We shall use LPG/CNG gas or electricity for heating our food because these are
efficient ways of supplying energy. The thermal efficiency of the energy source is
large, there is less pollution and the source can be used easily.
Question 4:
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Answer 4:
There are the following disadvantages of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum:
The burning of coal or petroleum causes air pollution.
Acidic oxides like oxides of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur are released on
burning fossil fuels. These oxides lead to acid rains, which affect our water
and soil resources.
Carbon dioxide gas also causes a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
Fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy.
Question 5:
Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Answer 5:
Fossil fuels, which have been traditionally used by human beings as an energy source, are non-renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are limited and cannot replenish on their own. They are being consumed at a large rate. If this rate of consumption continues, then fossil fuels would be exhausted from the Earth. Therefore, we should look for alternate sources of energy.
Question 6:
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our
convenience?
Answer 6:
To use the energy of flowing water large dams are built in hilly regions to store huge
amounts of water at a height. The stored water from the high level in the dam is carried
through pipes to the turbine at the bottom of the dam and runs a hydropower plant.
Similarly, wind energy is used to generate electricity. For the same purpose,
the rotatory motion of the windmill is used to tug the turbine of the electric generator.
Question 7:
What kind of mirror – concave, convex, or plain – would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Answer 7:
A solar cooker uses the heat of sunlight to cook food. A concave mirror is
used in order to reflect and focus sunlight on a particular area. The mirror focuses
all the incident sunlight at a point. The temperature at that point increases, thereby
cooking and heating the food placed in that particular area.
Question 8:
What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Answer 8:
Energy from the oceans can be obtained in the form of tidal energy, wave energy, and ocean thermal energy. But these energy sources suffer from the following
limitations:
There are very few locations where dams to utilize tidal energy can be built.
The cost of installation of powerhouses is extremely high and the efficiency of
plants is comparatively small.
Power plants built in oceans or at sea shores will need high continuous
maintenance as chances of corrosion are extremely high.
Question 9:
What is geothermal energy?
Answer 9:
Geothermal energy is the heat energy present inside the earth in certain regions called
hot spots. Due to geological changes, molten rocks formed in the deeper hot
regions of the earth’s crust are pushed upwards and are trapped in hot spots. When
underground water comes in contact with the hot spot, steam is generated. This
steam is routed through a pipe to a turbine and used to generate electricity.
Question 10:
What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Answer 10:
The advantages of nuclear energy are as follows:
A large amount of energy is produced per unit mass.
It does not produce smoke. It is clean energy.
The fission of one atom of uranium produces 10 million times the energy
released by the burning of one atom of carbon.
The fusion of four hydrogen atoms produces a huge amount of energy.
Sources Of Energy Class 9th: MCQs
Question 1.
Assertion: Fuel has to be burnt to obtain heat energy.
Reason: The minimum temperature to which a fuel must be heated so that it may catch fire and
start burning is known as ignition temperature.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
Answer
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Assertion: The major constituent of biogas is methane.
Reason: Biogas is produced by the aerobic degradation by animal wastes like cow ding in the
presence of water.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
Answer
(c) A is true but R is false.
Question 3.
Biogas is formed in the
(a) presence of air only
(b) presence of water only
(c) absence of air only
(d) presence of water and absence of air
Answer
(d) presence of water and absence of air
Question 4.
Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because
(a) biogas has lower calorific value.
(b) animal dung cake has a high calorific value
(c) biogas bums smoke and leave no residue
(d) biogas is used as a fuel for cooking only whereas dung cake can be used for cooking,
illuminant the lanterns.
Answer
(c) biogas bums smoke and leave no residue
Question 5.
Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) geothermal energy
(b) wind energy
(c) nuclear energy
(d) bio-mass
Answer
(c) nuclear energy
Question 6.
The working fluid in the ocean thermal power plant is
(a) Volatile liquid like ammonia
(b) petrol
(c) charcoal
(d) liquified petroleum gas
Answer
(a) Volatile liquid like ammonia
Question 7.
Ocean thermal energy is produced due to
(a) pressure differences at different levels in the ocean.
(b) temperature difference at different levels in the ocean.
(c) energy stored by waves in the ocean.
(d) tides rising out of the ocean.
Answer
(b) temperature difference at different levels in the ocean.
Question 8.
A device in which electricity is produced by the process of a controlled nuclear fission reaction is called
(a) nuclear chain reaction
(b) hydel power plant
(c) nuclear reactor
(d) thermal power plant
Answer
(c) nuclear reactor
Question 9.
India exploded her first underground nuclear device at
(a) Ranchi
(b) Kota
(c) Jaipur
(d) Pokhran
Answer
(d) Pokhran
Question 10.
A fusion reaction is also known as
(a) chemical reaction
(b) elastic scattering
(c) thermonuclear reaction
(d) photo nuclear reaction
Answer
(c) thermonuclear reaction
Question 11.
A good fuel should possess
(a) high ignition temperature
(b) moderate ignition temperature
(c) high calorific value
(d) both high calorific value and moderate ignition temperature
Answer
(d) both high calorific value and moderate ignition temperature
Question 12.
Geothermal energy is
(a) Heat energy in the interior of the earth
(b) the energy of molten mars exists in the form of magma inside the earth.
(c) molten lava on the surface of the earth
(d) energy obtained from solar thermal electric plants
Answer
(c) molten lava on the surface of the earth
Question 13.
Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam across
(a) narrow opening to the sea
(b) wide opening to the sea
(c) the river in hilly trains
(d) the river in plane areas
Answer
(a) narrow opening to the sea
Question 14.
The variety of coal which has the highest carbon content
(a) Anthracite
(b) Peat
(c) Bituminous
(d) Lignite
Answer
(a) Anthracite
Question 15.
Dead organisms are transformed into petroleum and natural gas in
(a) presence of air
(b) absence of air
(c) presence of sunlight
(d) none of the above
Answer
(b) absence of air
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a bio-mass energy source?
(a) gobar gas
(b) coal
(c) wood
(d) nuclear energy
Answer
(d) nuclear energy
Question 17.
The main constituent of CNG is
(a) butane
(b) methane
(c) ethane
(d) propane
Answer
(b) methane
Question 18.
Hydropower plants are located in the
(a) desert area
(b) plane area
(c) hilly terrains
(d) None of the above
Answer
(c) hilly terrains
Question 19.
The use of a reflector in the solar cooker is to
(a) Decrease efficiency
(b) create greenhouse effect
(c) increase efficiency
(d) None of the above
Answer
(c) increase efficiency
Question 20.
Solar cells are made of
(a) metals
(b) insulator
(c) semiconductors
(d) None of these
Answer
(a) Seine conductors
Question 21.
A solar cooker may not cook food if.
(a) Interior of the box and the container of food are perfectly shining.
(b) Glass sheet over the box is not closed.
(c) Solar cooker is placed in the shade.
(d) All the above
Answer
(d) All the above
Question 22.
Which of the following problem is associated with the burning of coal?
(а) Carbon-dioxide emission
(b) acid rain
(c) ash with toxic metal purity
(d) All of the above
Answer
(d) All of the above
Question 23.
Assertion: Wind energy farms cannot be established everywhere.
Reason: Wind energy farms can be established only at those places where the wind blows for the most part of the year.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
Answer
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 24.
Assertion: Coke is a better fuel than coal.
Reason: Burning of coke causes air pollution.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
Answer
(c) A is true but R is false.
Question 25.
Unit of calorific value of a substance is
(a) Kcal
(b) Joules
(c) J kg
(d) J/kg
Answer
(d) J/kg
Question 26.
The material used for the interconnection of the solar cells in the solar panel is
(a) silicon
(b) Silver
(c) aluminum
(d) copper
Answer
(b) silver
Question 27.
A solar panel is made by combining in an arrangement
(a) solar concentrator
(b) solar cookers
(c) solar cells
(d) solar chimney
Answer
(c) solar cells
Question 28.
Tidal energy is a form of energy obtained from the
(a) the motion of surface water in ponds
(b) ocean in the form of tidal waves
(c) tides occur in the river water
(d) the motion of the wave in sea
Answer
(b) ocean in the form of tidal waves
Question 29.
One major problem in harnessing nuclear energy is
(a) converting nuclear energy into electrical energy.
(b) sustaining the reaction.
(e) splitting the nuclei.
(d) disposing off spent fuel easily.
Answer
(d) disposing off spent fuel easily.
Question 30.
Which of the following is not an example of bio-mass energy?
(a) wood
(b) gobar-gas
(c) nuclear energy
(d) coal
Answer
(c) nuclear energy
Question 31.
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day
(b) a cloudy day
(c) a hot day
(d) a windy day
Answer
(b) a cloudy day
Question 32.
Which of the following gases is the main constituent of natural gas?
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c) Propane
(d) Butane
Answer
(a) Methane
Question 33.
Which of the following is the ultimate source of energy?
(a) Water
(b) Sun
(c) Fossil fuels
(d) Uranium
Answer
(b) Sun
Question 34.
The major problem in harnessing nuclear energy is to
(a) split heavy nucleus
(b) sustain nuclear reactions
(c) Convert nuclear energy into electricity
(d) dispose off spent fuel safety.
Answer
(d) dispose off spent fuel safety.
Question 35.
Which of the following is more environmentally friendly?
(a) Burning of coal
(b) burning of firewood
(c) burning of charcoal
(d) Burning of diesel.
Answer
(c) burning of charcoal
Question 36.
U-235 will undergo fission by
(a) low energy neutrons only
(b) high energy neutrons only
(c) medium energy neutrons
(d) low energy protons only
Answer
(d) low energy protons only
Question 37.
Which of the following organism produces biogas from cow drug sherry in the biogas plant?
(a) aerobic bacteria
(b) anaerobic bacteria
(c) protozoa
(d) fungi
Answer
(b) anaerobic bacteria
Question 38.
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but still, everybody discusses the energy crisis because
(a) Energy transform into different form continuously.
(b) Usable form of energy is dissipated to the surroundings in less usable forms.
(c) Energy is consumed and cannot be used again.
(d) All of the above
Answer
(d) All of the above
Question 39.
The temperature inside the solar cooker ranges from
(a) 500-100°C
(b) 100-140°C
(c) 150-200°C
(d) 70-80°C
Answer
(b) 100-140°C
Question 40.
Select the important factor for the site selection of a thermal power plant.
(a) Distance from the populated area
(b) Availability of fuel
(c) Availability of water
(d) Cost of plant
Answer
(c) Availability of water
Question 41.
The wind is caused due to
(a) uneven heating of the earth’s surface
(b) rotation of earth
(c) local conditions
(d) All of the above
Answer
(d) All of the above
Question 42.
Solar cells are made of
(a) germanium
(b) silicon
(c) Silver
(d) aluminum
Answer
(b) silicon
Question 43.
What is the disadvantage of solar energy
(a) A large surface area is required to collect the solar
(b) Daily average of solar energy varies from 4 to 7 kWh/m2
(c) Highly hazardous toxic material is used in the manufacturing of solar devices.
(d) All of the above
Answer
(d) All of the above
Question 44.
An ideal source of energy should have
(a) higher calorific value
(b) easy transportability
(c) easy accessibility
(d) All the above
Answer
(d) All the above
Question 45.
Radiations that are harmful to the living organisms are
(a) Infrared radiation.
(b) ultraviolet radiations
(c) Visible radiation.
(d) micro waves
Answer
(b) ultraviolet radiations
Conclusion
We have shared all about Sources Of Energy Class 10th Science NCERT notes to help the students with the lesson as well as we have also provided NCERT Solutions For Class 10th Science chapter Sources Of Energy. We also provide some important diagrams of Sources Of Energy Class 10th to help the students with the crux of the lesson and be able to attempt the questions in the board examinations.