We are providing you with the detailed notes of geography lesson 1 resources and development class 10 along with the ncert solutions, multiple-choice questions, and some value-based questions so that the students can cope with the new assessment scheme. Students after going through these short notes will be able to understand the new pattern and the concepts will be on fingertips.
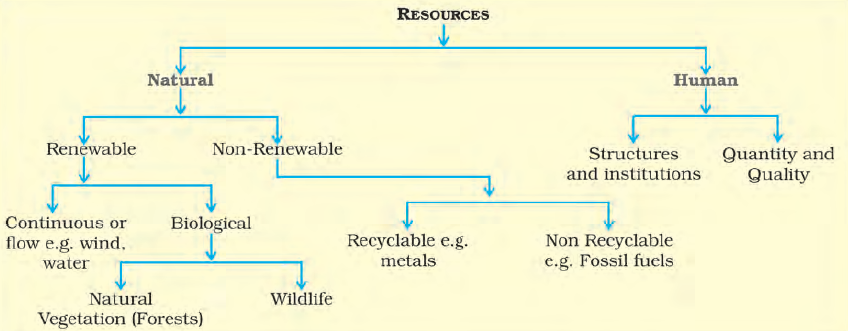
What are Resources and What are their types?
Resource- Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable can be termed as a resource.
Types of resources–
These resources can be classified in the following ways-
- Based on origin- biotic and abiotic
- Based on exhaustibility- renewable and non-renewable
- Based on ownership- individual, community, national and international
- Based on the status of development- potential developed stock and reserves.
Biotic resources are obtained from the biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora, and fauna, fisheries, livestock, etc.
All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example- rocks and metals.
Renewable resources can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical, or mechanical processes. For example; solar and wind energy, forests, and wildlife, etc.
Non-renewable resources occur over a long period of time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation.
Individual resources are owned privately by individuals. For example; many farmers own land which is allotted to them by the government against the payment of revenue.
Community-owned resources are resources that are accessible to all the members of the community. Example- village commons, public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas, etc.
National resources technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The computer has legal powers to acquire even private property for the public good.
International resources are international institutions that regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 KM of Exclusive Economic Zone to open oceans and no individual country can utilize these without the occurrence of international institutions.
Potential resources- resources that are found in a region, but have not been utilized. For example; the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat. Have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly.
Developed resources- these are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilization.
Development of resources
Resources are vital for human survival as well as for maintaining the quality of life. It was believed that resources are gifts of nature. Human beings used them indiscriminately and this has led to the following major problems:
- Depletion of resources for satisfying
- Accumulation of resources in few hands, which in turn, divided the society into two segments i.ee. Haves and have not or rich and poor.
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution, and land degradation.
Resources planning in India-
- Identification and inventory across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping, and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
- Evolving planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill, and institutional setup for implementing resource developmental plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national developmental plans.
Conservation of resources-
- Resource conservation at various levels is important.
- Gandhi was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation in these words: “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed”
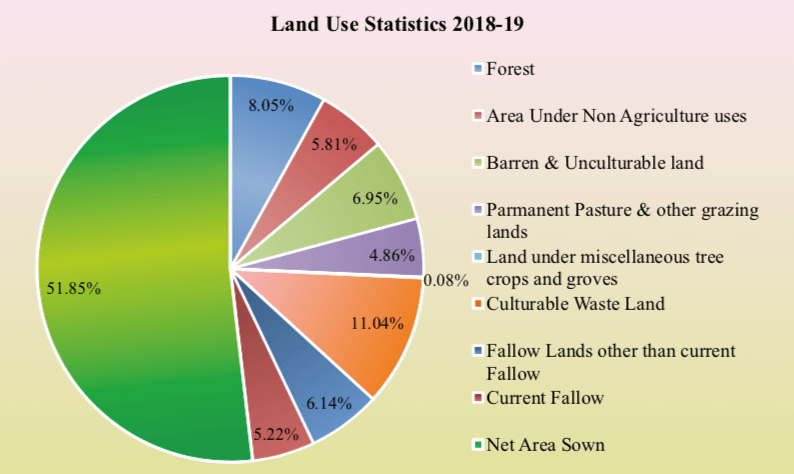
Land Utilization-
Land resources are used for the following purposes-
Forests
Land not available for cultivation-
- Barren and wasteland
- Land put to non-agricultural uses: buildings, roads, factories. Etc.
- Other uncultivated lands ( excluding fallow land )
- Permanent pastures and grazing land
- Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves( not included in the net sown area)
- Other than current fallow land which is left for th past 1 to 5 agricultural year.
- Net sown area – area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus the sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Land use pattern in India-
- The total geographical area of India is 3.28 Million sq. km.
- Land use data however is available only for 93% of the total area because the land use reporting for most of the Northeast states except Assam has not been done fully surveyed.
- Some are of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
- The land under permanent pasture has also decreased.
- Fallow land- left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year.
- Net sown area total- total area seen in an agricultural year.
- More net sown area in Punjab and Haryana.
- Less net sown area in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman, and Nicobar islands.
- National Forest Policy in India in 1952.
- Wasteland includes rocky, arid, and desert areas, and land put to other non-agricultural uses include settlements, roads, railways, industry, etc.
- Continuous use of and over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it.
Land degradation and conservation measures-
At present, there are about 130 million hectares of degraded land in India.
Some human activities such as deforestation, over-grazing, mining, and quarrying have contributed significantly to land degradation.
In states, like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Orissa deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation.
In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra overgrazing are one of the main reasons for land degradation.
In the states of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation.
NCERT SOLUTIONS For Resources and Development Class 10th
Q1. Multiple-choice questions-
1. Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore?
- Renewable
- Flow
- Biotic
- Non-renewable
Ans- Non-renewable
2. Under which of the following type of resources can tidal energy be puy?
- Replenishable
- Abiotic
- Human-made
- non-recyclable
Ans- Replenishable
3. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
- Intensive cultivation
- Over irrigation
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing
Ans- over-irrigation
4. In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practiced?
- Punjab
- Harayana
- Plains of Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
Ans- Uttarakhand
5. In which of the following states is black soil found?
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Jharkhand
Ans- Gujarat
Q2. name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it?
Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhatisgarh.
Q3. what type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Alluvial soil is found in the river delays of the eastern crops. Alluvial soil is rich in p[otash, phosphoric acid, and lime. It has a high water retention capacity and is highly fertile soil.
Q4. what steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Terrace farming and shelterbelts.
Q5. what are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give examples?
Biotic resources- All living organisms in our environment are called biotic resources. For example; trees, animals, insects, etc.
Abiotic resources- All non-living things present in our environment are termed biotic resources. For example- earth, air, water, metals, rocks, etc.
Q6. Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
About 45% of the land is used as net sown area, i.e. for farming. About 22% of the land is under forest and the rest of the land is used for various purposes; like housing, recreation, and industrial activities. Increasing population and subsequent increase in demand for resources is the main reason that forested land has not increased much during this period.
Q7. How has technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Economic development creates demand for various resources and technical development gives the knowledge to exploit those resources.
Thus, technical and economic development; together lead to more consumption of resources.
Multiple Choice Questions For Resources and Development
1. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of:
Any country
Any state
Any region
None of the above
Ans- any region
2. Some countries colonized other countries because of their:
- Natural beauty
- Money
- Rich resources
- None of the above
Ans- rich resources
3. In which of the following books, Schumacher presented Gandhian philosophy
- Big is beautiful
- Large is beautiful
- Small is beautiful
- Everything is beautiful
Ans- small is beautiful
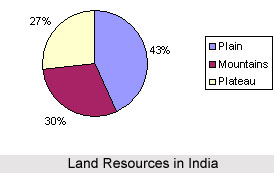
4. What % of Indian land areas is plain area :
- 40%
- 41%
- 42%
- 43%
Ans- 43%
5. What % of Indian land area is mountain area:
- 10%
- 20%
- 30%
- 40%
Ans- 30%
6.What is the total geographical area of India?
- 2.28 million sq. km.
- 3.28 million sq. km.
- 4.28 million sq. km.
- 5.28 million sq. km.
Ans- 3.38 million sq. km.
7.What % of Geographical area is desired forested area?
- 23 percent of geographical area
- 33 percent of geographical area
- 43 percent of geographical area
- 53 percent of geographical area
Ans- 33 percent of geographical area
8.How many million hectares of Indian land is degraded land?
- 110 million hectares
- 120 million hectares
- 130 million hectares
- 140 million hectares
Ans- 130 million hectares
9. Which of the following is the main reasons for land degradation in the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, M.P., and Maharashtra?
- Deforestation
- Floods
- Over-grazing
- All of the above
Ans- over-grazing
10. Which is the most widely spread and important soil?
- Black
- Red
- Alluvial
- Desert
Ans- alluvial
11. The soil which has a higher concentration of Kanker nodules is called-
- Hangar
- Khadar
- Alluvial soil
- Red soil
Ans- hangar
12. Black soil is also known as-
- Regur
- Khadar
- Bhangar
- All of the above
Ans- regur
13. The soil which develops in areas with high temperatures and heavy rainfall is called-
- Regur
- Alluvial
- Laterite
- Arid
Ans- laterite
14.Red laterite soil is suitable for growing which of the following crops-
- Coffee
- Tea
- Wheat
- Cashew nuts
Ans- cashew nuts
15. When the topsoil is washed away when water flow as a sheet over large areas down a slope is known as-
- Land erosion
- Water erosion
Sheet erosion - All of the above
Ans- sheet erosion
16. Resources are a function of –
- National activities
- Human activities
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Ans- human activities
17. Biotic resources are obtained from-
- Biosphere and include living organisms
- Biosphere and include non-living organisms
- The earth
- None of the above
Ans- Biosphere and include living organisms
18. Rocks and metals are examples of-
- Biotic resources
- Abiotic resources
- Natural resources
- All of the above
Ans- abiotic resources
19. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by the government:
- Against the payment by cash
- Against property in towns
- Against the payment or revenue
- None of the above
Ans- against the payment of revenue
20. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells, etc are some examples of-
- Resources owned by the government
- Resources owned by the private
- Resources owned by individual
- None of the above
Ans- resources owned by individual
21. Resources that are accessible to all the embers of the community are called-
- Private owned resources
- Public owned resources
- Community-owned resources
- Individual owned resources
Ans- community-owned resources
22. Resources belonging to the nation are called-
- State resources
- Country resources
- National resources
- Individual resources
Ans- national resources
23. Resources that are found in a region, but have not been utilized are called-
- Developed resources
- Stock
- International resources
- Potential resources
Ans- potential resources
24. Resources that are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilization are called-
- Potential resources
- Developed resources
- Stock
- International resources
Ans- developed resources
25. Materials in the environment that have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technical knowhow to access them are called-
- Resources
- Stock
- Reserves
- All of the above
Ans- stock
Value-Based Questions For Resources and Development
To follow the new assessment scheme we are also jotting down some value-based questions of class 10 th lesson Resources and development to help the students.
Q1. What was the main contribution of the Brundtland Commission Report, 1987?
The seminal contribution concerning resource conservation at the global level was made by the Brundtland Commission Report, 1987.
This report introduced the concept of Sustainable development and advocated it is as a means for resource conservation, which was substantially published in a book, entitled Common Future.
Q2. Resources are a function of human activities. Elaborate the statement with suitable arguments.
- Natural resources are the gifts of nature but many man-made resources are used by humanity.
- Resources are functions of human activities. Human beings themselves are essential components of resources.
- They transform materials available in our environment into resources and use them.
Q3. What was agenda 21?
- It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED).
- I focus on attaining Global sustainable development.
- Its main aim is to fight environmental damage, poverty, diseases through global cooperation on common interest, mutual needs, and shared responsibilities.
- An important and distinct aim of the agenda is that every local government should draw its own local agenda 21.
Q4. Write a short note on Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, 1992.
- Rio de Janerio was the meeting ground for the first international Earth Summit.
- More than 100 heads of state met at this famous conference which was convened in June 1992 to address the urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
- A declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity was signed by the assembled leaders.
- They adopted Agenda 21 and endorsed the global forest principles to achieve sustainable development in the 21st century.
Q5. Explain the relationship between the process of colonization and the rich resources of colonies?
The history of colonization reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions of the foreign traders.
It was primarily the higher level of technological development of colonizing countries that helped them to exploit the resources of other regions and established their supremacy over colonies.
Their fore resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes.
Case Study Questions For Resources and Development
Read the extract given below and answer the following questions
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generation too. Ninety-five percent of our basic needs of food, shelters, and clothing are obtained from the land.
Human activities have not only brought about the degradation of the land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to the land. Some human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and quarrying too have contributed significantly and land degradation.
Mining sites are abandoned, after excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars and traces over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, M.P., and Odisha, deforestation sure to mining has caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, M.P., and Maharashtra overgrazing are one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states like Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to waterlogging leading to an increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Answer the questions-
1. Most of the basic needs for food, shelter, and clothing are obtained from
- Land
- Human activities
- Mining
- Land degradation
Ans- Land
2. Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation in the state of-
- Jharkhand
- U.P.
- Punjab
- Haryana
Ans-Jharkhand
3. Over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to the following reasons-
- Deforestation and over grazing’
- Increase in alkalinity of the soil
- Waterlogging leading to an increase in salinity in soil
- Noen of these
Ans- water logging due to an increase in salinity of the soil
4. Human is considered as the main culprit for land degradation because
- Of his excavation work at mining sites
- Of his significant contribution to deforestation
- He has aggravated the pace of natural forces causing damage to land
- All of these.
Ans- he has aggravated the pace of natural forces causing damage to land
Conclusion
We have penned down the summary of the lesson resources and development class 10 along with the ncert solutions and MCQs. we have also mentioned some value-based questions. Students after reading the lesson can go through these to get the gist of the lesson at just one stroke.

